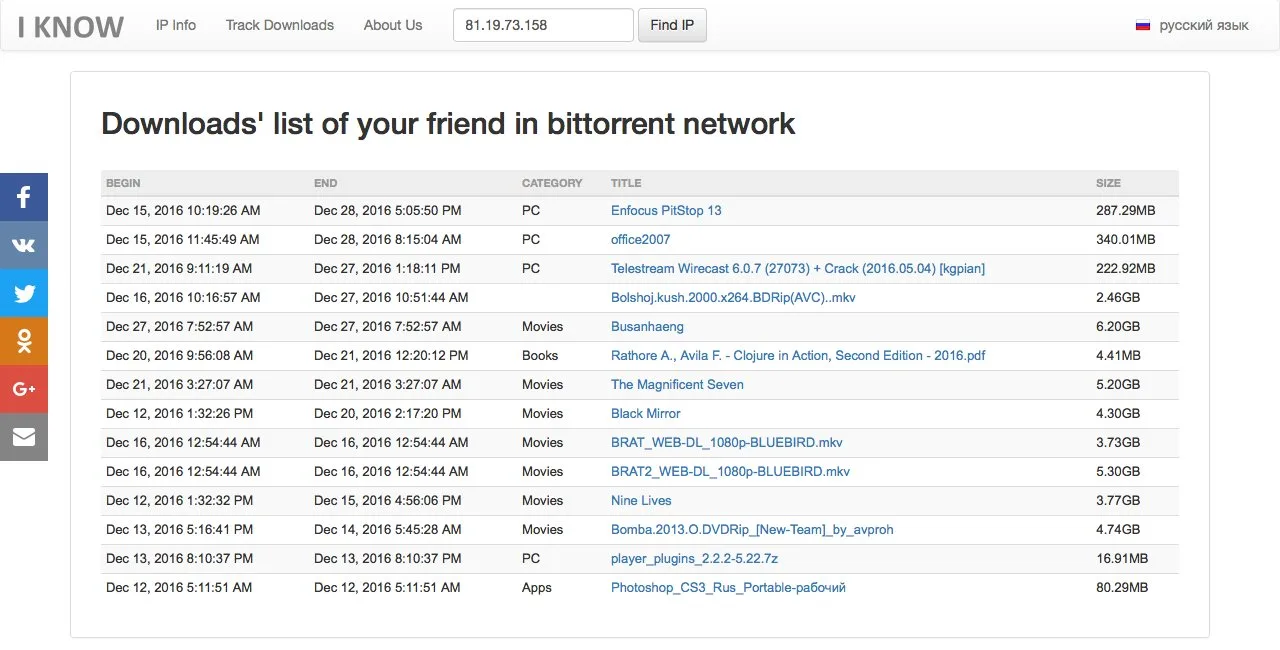
Google Gemini for Workspace can be used to create brief email summaries that appear legitimate but contain malicious instructions and messages directing users to phishing sites.
This attack uses prompt injections hidden in emails, which Gemini follows when generating a summary of the message.
Information security specialist Marco Figueroa discussed the vulnerability of Google Gemini to prompt injections. Figueroa is the manager of the 0Din (0Day Investigative Network) bug bounty program. This program was launched by Mozilla in the summer of 2024 and serves as a reward program for identifying vulnerabilities in large language models (LLM) and other deep learning technologies and tools.
The attack is based on crafting an email with an invisible directive for Gemini. The attacker can conceal a malicious instruction for the AI within the email text, at the end of the message, by using HTML and CSS to set the font size to zero or color it white.
Such a malicious instruction will not be displayed in Gmail and will not be noticeable to a person. However, since there are no suspicious attachments or links in the email, the message is highly likely to reach the recipient’s inbox.
If the recipient opens the email and asks Gemini to create a brief summary, the AI will read the invisible instruction and execute it.
In Figueroa’s example, Gemini follows hidden instructions in the email and displays a warning to the user that their Gmail password may have been compromised. This message is accompanied by a fake customer support phone number.
Since users generally trust the results provided by Gemini, which is part of the Google Workspace functionality, there is a high likelihood that such a warning will be perceived as genuine.
An expert suggests several methods for detecting and mitigating such attacks. One of these involves removing, neutralizing, or ignoring content in emails that is formatted as hidden text. Another method involves using a post-processing filter that scans the Gemini output for warnings, URLs, or phone numbers, flagging such messages for further review.
Additionally, users should remember that the brief summaries from Gemini should not be considered reliable, especially when it comes to any warnings related to security.
Google representatives assured the media that the company is working on protection against such attacks.
“We are continuously strengthening our already robust defenses by conducting red team tests, during which our models are trained to counteract such attacks,” Google representatives report.
Google also noted that the company is not aware of any cases of Gemini manipulation as described in Figueroa’s report.