The technique was first discovered in February 2025, but its spread rate is continuously growing, and currently attackers abuse MU plugins to run three different types of malicious code.
Must-Use Plugins represent a special type of WordPress plugins that run every time the page is loaded and don’t require activation in the Admin Panel. These PHP files are stored in the wp-content/ directory, are executed automatically, and don’t appear in the Admin Panel on the Plugins page unless the Must-Use filter is selected.
Among other things, such plugins are used to enforce custom security rules across the website, boost performance, dynamically modify variables, etc.
Since MU plugins are executed on every page load and don’t appear in the standard plugin list, they can be used to covertly perform a wide range of malicious operations (e.g. steal credentials, inject malicious code, or modify HTML output).
Sucuri experts discovered three different payloads placed by cybercriminals to the MU-plugins directory:
-
redirect.redirects visitors (excluding bots and logged in admins) to the malicious website updatesnow[.]net that displays a fake browser update prompt to trick the victim into downloading malware;php -
index.is a web shell that acts as a backdoor by downloading and executing PHP code from a GitHub repository; andphp -
custom-js-loader.loads JavaScript that replaces all images on the website with explicit content, hijacks all external links, and opens fraudulent pop-ups instead.php
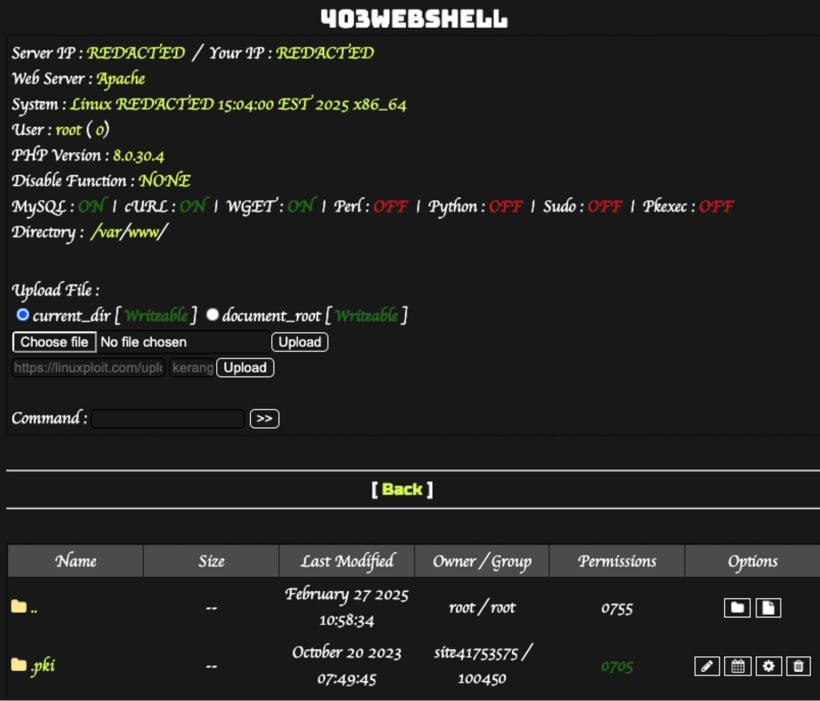
The most dangerous payload is the web shell since it enables attackers to remotely execute commands on the server, steal data, and deliver subsequent attacks on resource users and visitors.
The other two malware samples are more likely to damage the website’s reputation and its SEO rankings due to suspicious redirects and attempts to install malware on visitors’ computers.
The infection technique used by the malefactors remains unknown yet. Its assumed that the attackers exploit known vulnerabilities in WordPress plugins and themes or weak admin credentials.
