“At issue are identities that lack registry permissions but that have edit permissions on Google Cloud Run revisions. The vulnerability could have allowed such an identity to abuse its Google Cloud Run revision edit permissions in order to pull private Google Artifact Registry and Google Container Registry images in the same account,” – Tenable Research
The vulnerability dubbed ImageRunner was reported to Google and fixed on January 28, 2025.
Tenable Research experts call ImageRunner an example of the Jenga concept: multiple cloud services are closely interrelated, which inevitably creates severe risks.
“Cloud providers build their services on top of their other existing services. Sometimes they create “hidden services.” If one service gets attacked or is compromised, the other ones built on top of it inherit the risk and become vulnerable as well. This scenario opens the door for attackers to discover novel privilege escalation opportunities and even vulnerabilities, and introduces new hidden risks for defenders,” – Tenable Research.
Google Cloud Run is a fully managed platform that enables you to run containerized applications in a scalable serverless environment on top of Google’s infrastructure. Container images are pulled from Artifact Registry (or Docker Hub) for subsequent deployment by specifying an image URL.
As said above, some accounts don’t have access to Container Registry, but can edit Google Cloud Run revisions. Every time a Cloud Run service is deployed or updated, a new version is created. And every time a Cloud Run revision is deployed, a service account is used to pull the required images.
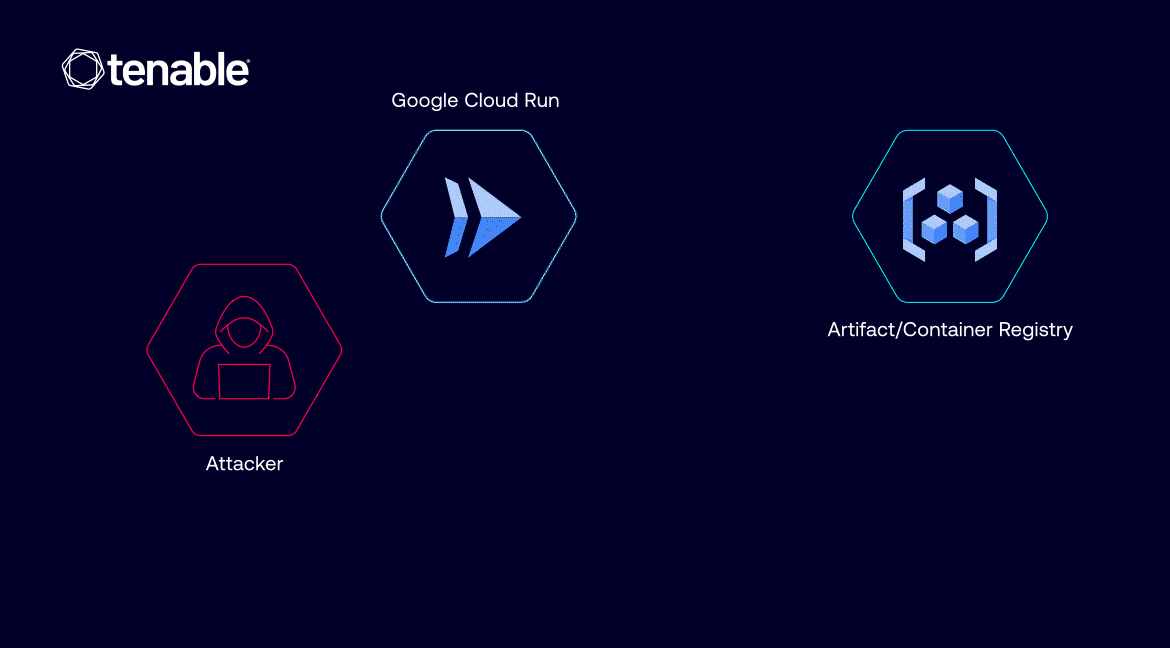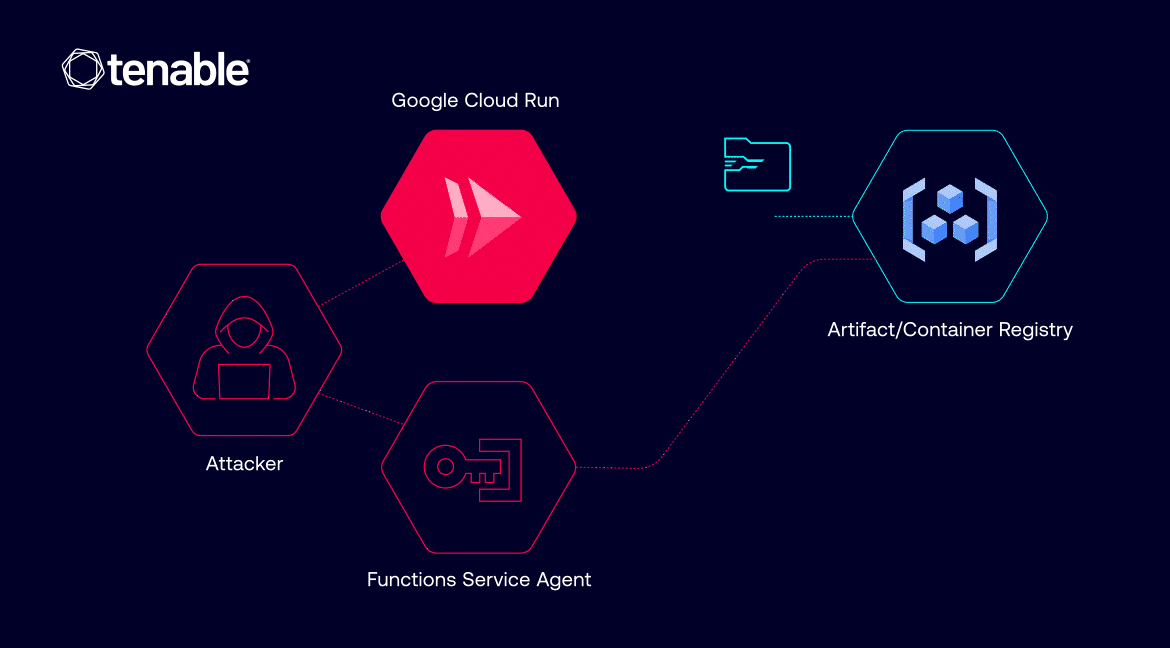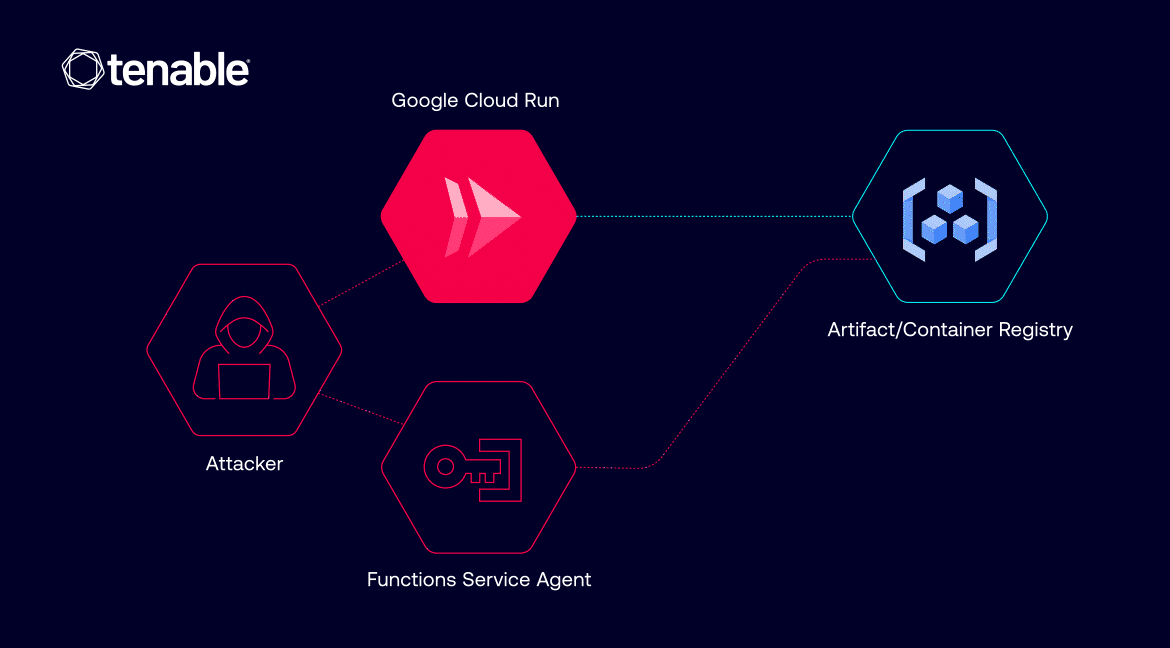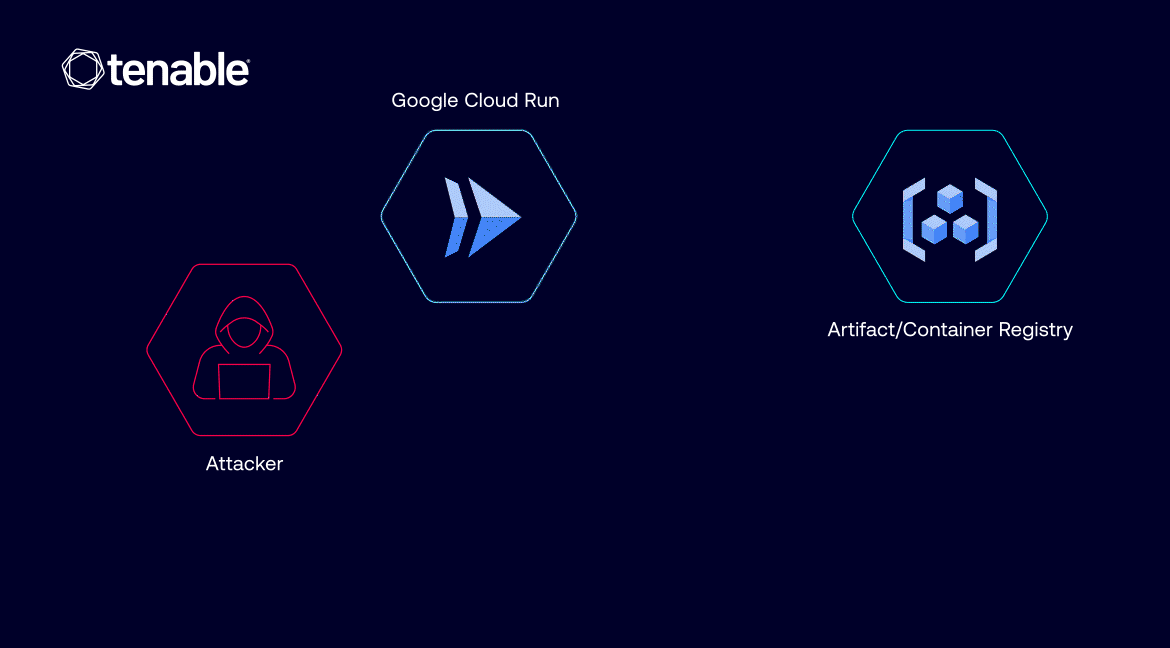
“If an attacker gains certain permissions within a victim’s project – specifically run.services.update and iam.serviceAccounts.actAs permissions – they could modify a Cloud Run service and deploy a new revision. In doing so, they could specify any private container image within the same project for the service to pull,” – Tenable Research.
Attackers can access sensitive or proprietary images stored in a victim’s registries and inject malicious instructions to extract secrets, steal sensitive data, or even start a reverse shell.
The patch released by Google ensures that any user or service account creating or updating Cloud Run has explicit permission to access container images.
