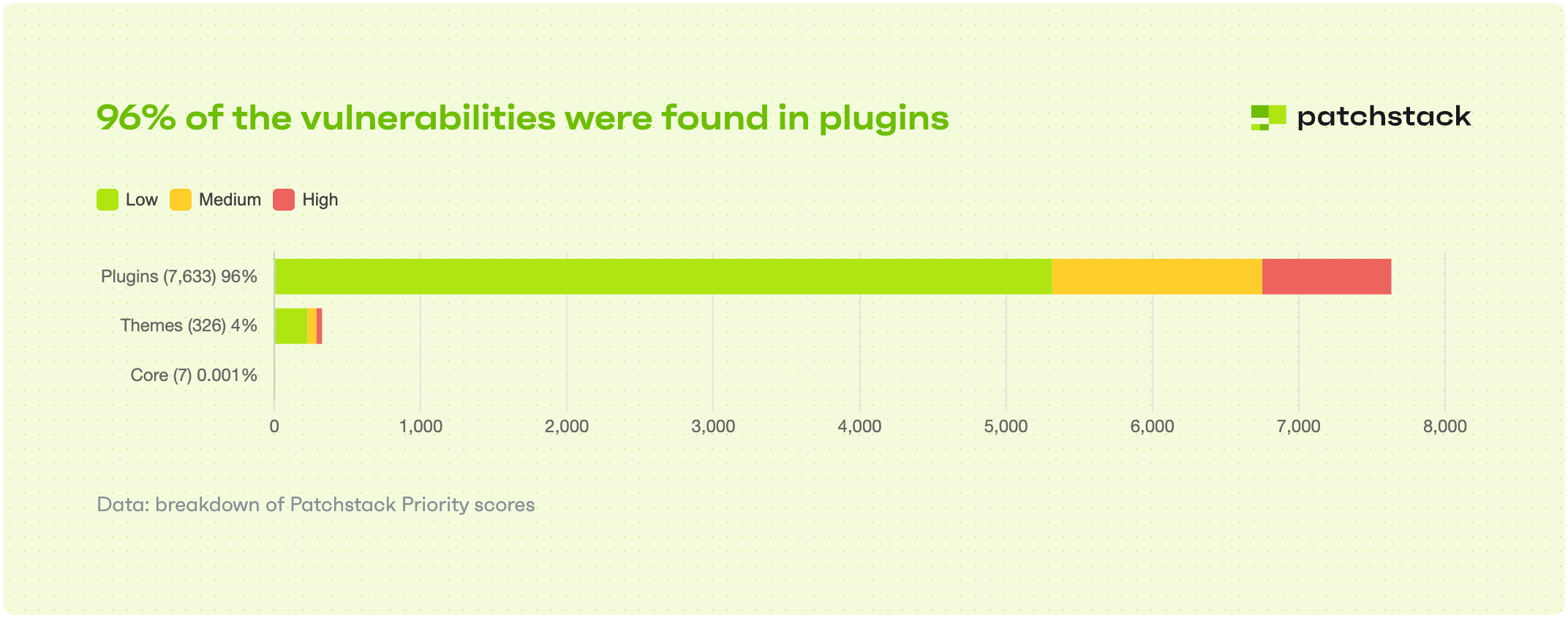
Experts note that only seven vulnerabilities discovered last year affected the WordPress core. Most of the security holes were discovered in plugins (7,633 vulnerabilities or 96% of their total number); and only a small proportion of them, in themes (326 vulnerabilities or 4% of their total number).
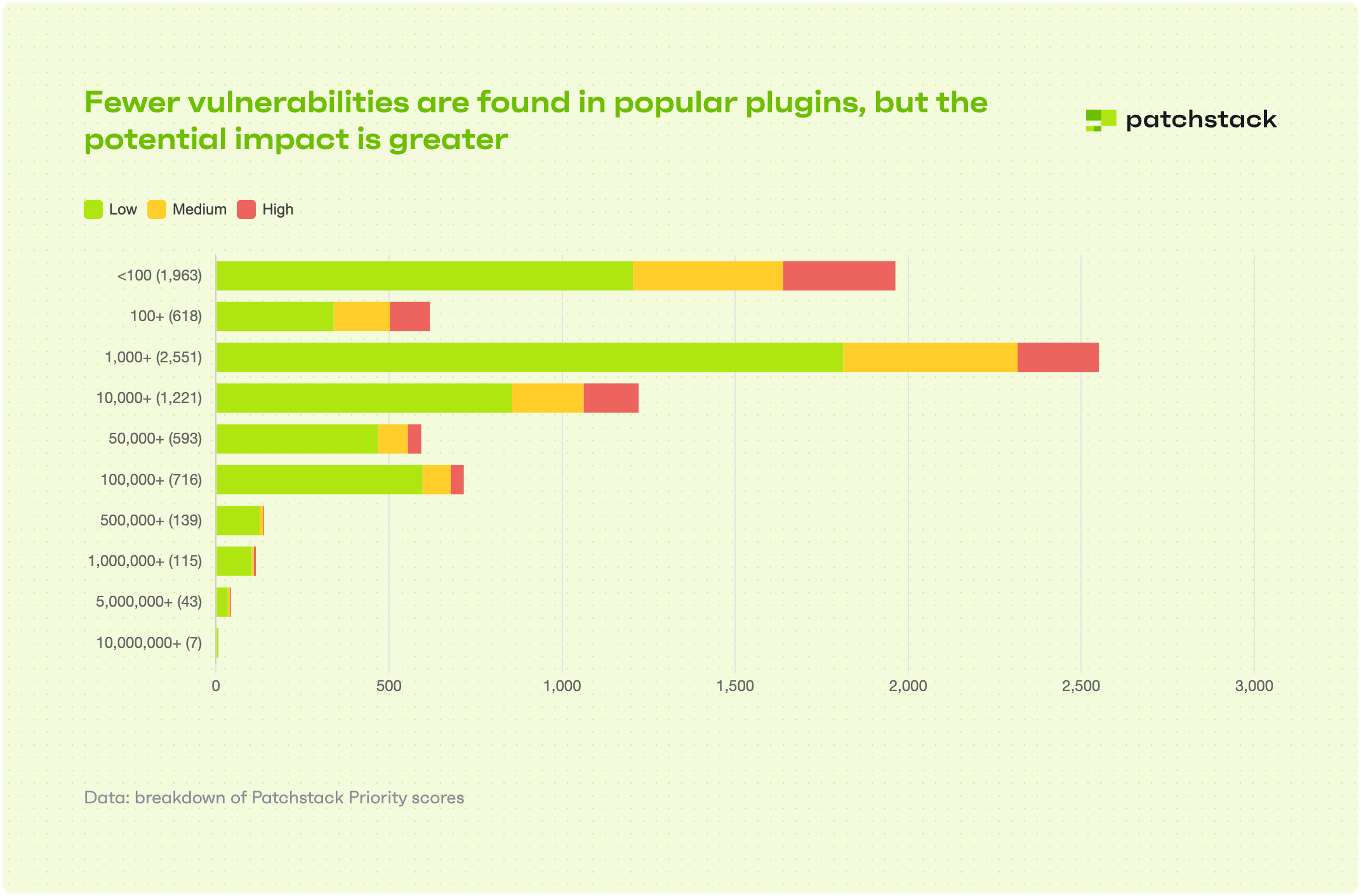
In total, 1,018 bugs were identified in plugins installed more than 100,000 times; while other 115 vulnerable plugins were installed more than 1 million times each, including seven plugins with 10 million installations.
Patchstack experts claim that, despite the impressive number of vulnerabilities, most of them didn’t pose significant threats: 69.6% of the bugs were unlikely to be exploited; other 18.8% could be used in targeted attacks; and only 11.6% were actually used in attacks or recognized likely to be exploited.
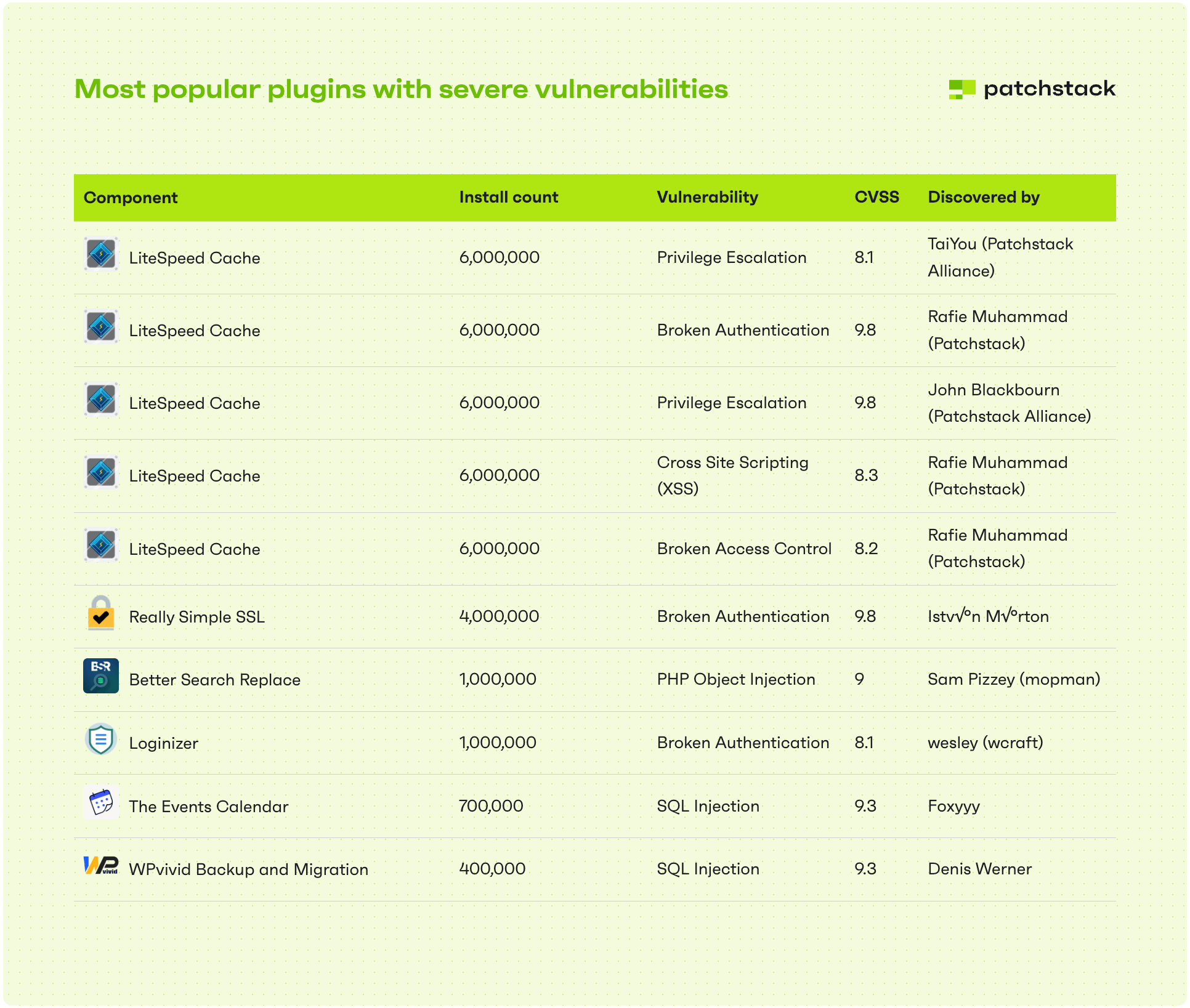
Only one-third of the identified vulnerabilities had high-risk or critical CVSS scores.
Patchstack reports that 43% of all security holes discovered in WordPress in 2024 could be exploited without authentication; only some bugs required interaction with an authenticated user.
Other 43% of vulnerabilities required at least low privileges (e.g. contributor or subscriber) to be exploited; while 12% of them required administrator, author, or editor privileges.
Almost half of the WordPress issues documented in 2024 were related to XSS (47.7%); access control violation (14.19%) and CSRF (11.35%) bugs were widespread as well.

Patchstack analysts emphasize that developers of WordPress plugins must take prompt actions to ensure the security of their users. The fact is that last year, 33% of identified vulnerabilities remained unfixed until their public disclosure.