On RubyGems, 60 malicious packages were discovered that masqueraded as harmless tools for automating social networks, blogs, and messengers. The gems stole users’ credentials and, since March 2023, have been downloaded more than 275,000 times.
Experts at the company Socket, who observed this campaign, report that the packages were primarily aimed at users in South Korea who use automation tools to work with TikTok, X, Telegram, Naver, WordPress, Kakao, and so on.
The full list of malicious packages can be found in Socket’s report. Below are examples of typosquatting used by the attackers.
- WordPress automation: wp_posting_duo, wp_posting_zon.
- Telegram bots: tg_send_duo, tg_send_zon.
- SEO tools for backlinks: backlink_zon, back_duo.
- Tools for blog platforms: nblog_duo, nblog_zon, tblog_duopack, tblog_zon.
- Tools for Naver Café: cafe_basics[_duo], cafe_buy[_duo], cafe_bey, *_blog_comment, *_cafe_comment.
The malware was published on RubyGems.org under the names of various publishers: zon, nowon, kwonsoonje, and soonje. Distributing the malicious activity across multiple accounts made tracking and blocking the attacks more difficult.
It is emphasized that all 60 gems had a graphical user interface that looked legitimate and implemented the advertised functionality. At the same time, all data entered by victims into login forms was transmitted to hard-coded addresses of the attackers’ servers (programzon[.]com, appspace[.]kr, marketingduo[.]co[.]kr).

In some cases, the tools also displayed error or success messages, even though they did not actually perform any logins or API requests.
Ultimately, usernames and passwords were transmitted in plaintext to the malware operators, along with device MAC addresses (for fingerprinting) and the names of the malicious packages (to track the effectiveness of the campaign).
Researchers note that they have found the stolen data for sale on Russian-language darknet marketplaces.
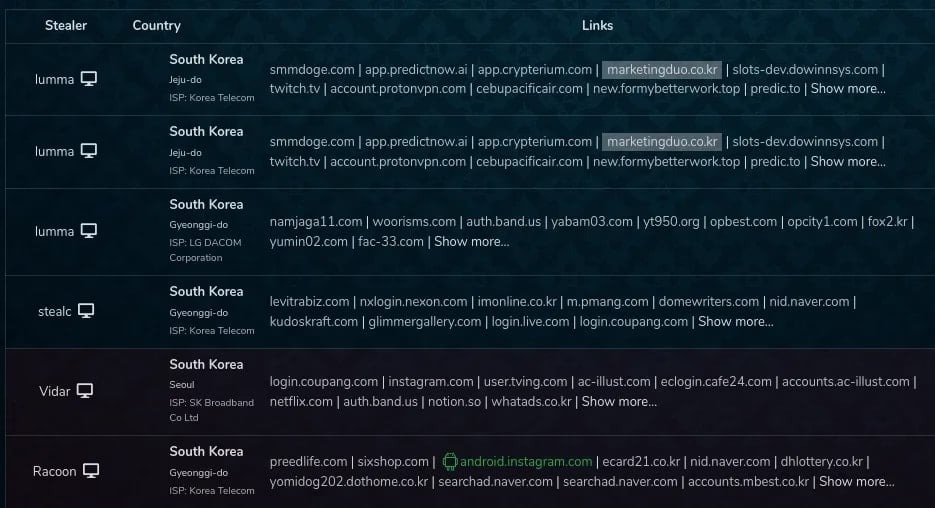
The report notes that at least 16 of the 60 malicious gems remain available for download, even though Socket notified the RubyGems team about all of the malicious packages.
Experts remind developers to always carefully scrutinize packages from open-source repositories for suspicious code (e.g., obfuscation), consider the author’s reputation and release history, and rely on versions that have already been vetted and are known to be safe.
