Analysts from Beazley Security and SentinelOne have warned about a campaign distributing an updated version of the PXA Stealer infostealer, written in Python. According to the researchers, the stealer has already compromised over 4,000 victims across 62 countries worldwide.
Researchers believe that Vietnamese-speaking hackers are behind PXA Stealer. They monetize the stolen data from victims by selling it to other criminals through Telegram and even have their own subscription-based system.
“This discovery demonstrates significant progress in attack tactics: more advanced anti-analysis methods are now being used, alongside harmless fake content for lures and secure command infrastructure, which delays detection and complicates investigation,” experts say.
Currently, the stealer’s activity has impacted over 4000 unique IP addresses across 62 countries (including South Korea, the USA, the Netherlands, Hungary, and Austria). PXA Stealer has stolen: over 200,000 unique passwords, data from hundreds of bank cards, and more than 4 million browser cookies from victims.
PXA Stealer was first discovered by analysts from Cisco Talos in November 2024. At that time, it was primarily used for attacks on government and educational institutions in European and Asian countries. This malware is capable of stealing passwords, browser autofill data, cryptocurrency wallet information, and data from banking applications.
The stolen data is transmitted to the malware operators via Telegram, and then ends up on hacker platforms like Sherlock, which trade in logs. Other cybercriminals can purchase them there, for instance, to steal cryptocurrency or to conduct further attacks on organizations.
According to Beazley Security and SentinelOne, by 2025, the distribution tactics of stealers became more sophisticated. Attackers started using DLL side-loading and multi-stage malware execution schemes to remain undetected for longer periods.
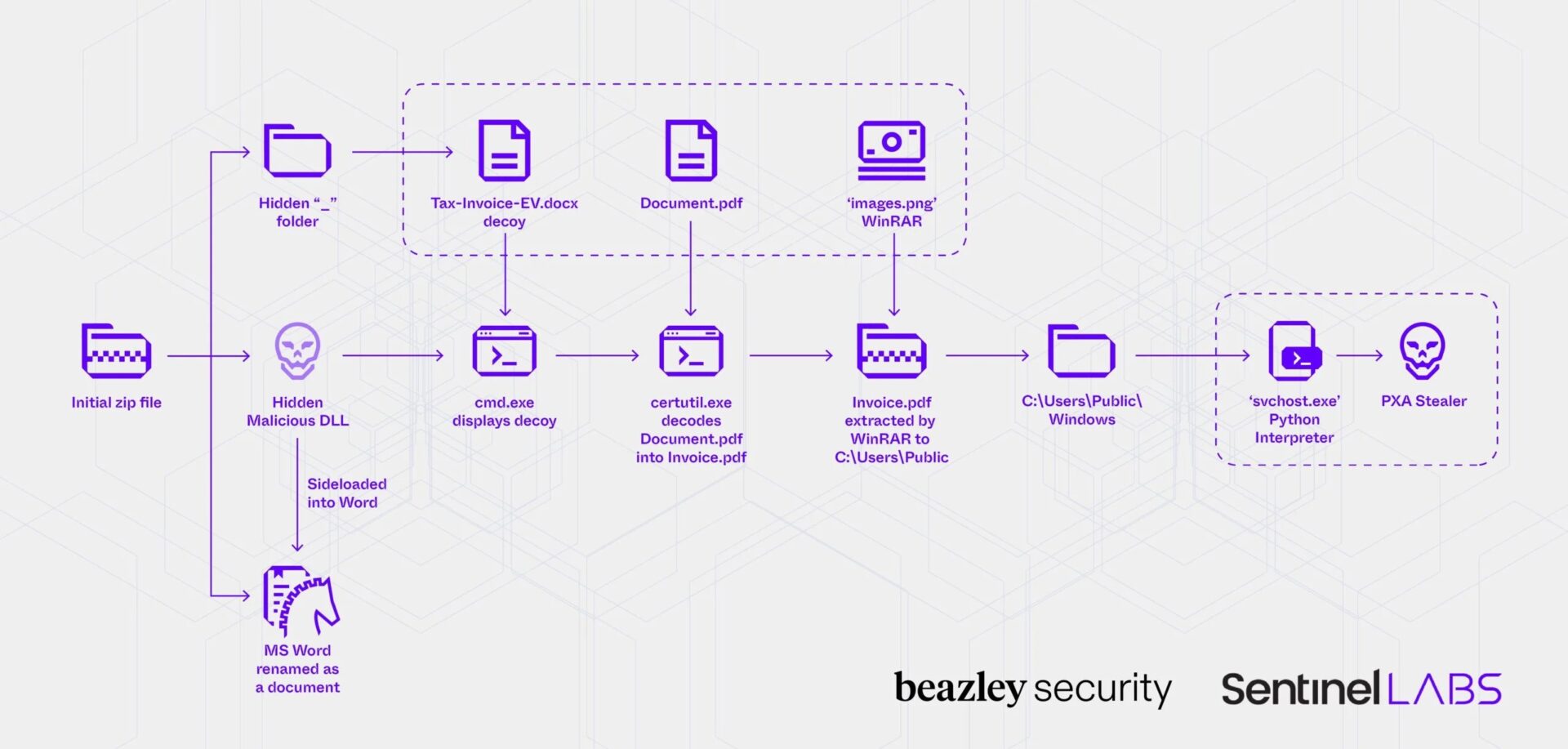
For instance, in April of this year, attackers used phishing emails to trick victims into downloading an archive containing a signed copy of Haihaisoft PDF Reader along with a malicious DLL library.
The malicious DLL is responsible for carrying out all the infection steps and at some point presents the victim with a decoy (such as a fake copyright infringement notification). After this, the stealer is deployed into the system.
Moreover, the updated version of PXA Stealer can extract cookies from Gecko and Chromium-based browsers (by injecting DLL into running processes, bypassing the protection of App-Bound Encryption) and steals data from VPN clients, cloud CLI interfaces, connected network resources, as well as several other applications, including Discord.
“PXA Stealer uses bot identifiers (TOKEN_BOT) to link the main bot with Telegram channels (CHAT_ID),” the researchers explain. “Different channels in Telegram are behind the ChatID, but they are mainly used for receiving stolen data and sending notifications to operators. The idea of using the legitimate infrastructure of Telegram is driven by the desire to automate data theft and simplify the process of selling it, which allows cybercriminals to deliver information to other criminals more efficiently.”
