According to Veracode, since the beginning of May, the malicious os-info-checker-es6 package has been downloaded more than 1,000 times. Interestingly, the first version of this package added to npm on March 19 was relatively safe: it only collected information about the host.
Since then, the authors modified the package by including platform-specific binaries and obfuscated installation scripts. As a result, its new version published on May 7, 2025 contains sophisticated code for communication with the C&C server from where the final payload is delivered.
The latest version of malicious os-info-checker-es6 (1.0.8) is still available on npm.
What’s worse, the malicious package is listed as a dependency for four other npm packages: skip-tot, vue-dev-serverr, vue-dummyy, and vue-bit. All of them are marketed as useful development and accessibility tools. The researchers were unable to determine whether these utilities are related to the same malicious campaign.
The malicious version of os-info-checker-es6 embeds data in a string that appears to be a single vertical bar ‘|’. However, this character is followed by a long sequence of invisible Unicode characters from the Variation Selectors Supplement range (U+E0100 to U+E01EF).
Typically, such characters are used as modifiers for preceding characters to provide specific glyph variations in complex scripts. In this malware, their function is to facilitate steganography (i.e. conceal information among other data).
Veracode experts decrypted and deobfuscated the long string of invisible characters revealing a payload for a sophisticated C&C mechanism that uses a Google Calendar event short link as a dynamic dropper for its final payload.
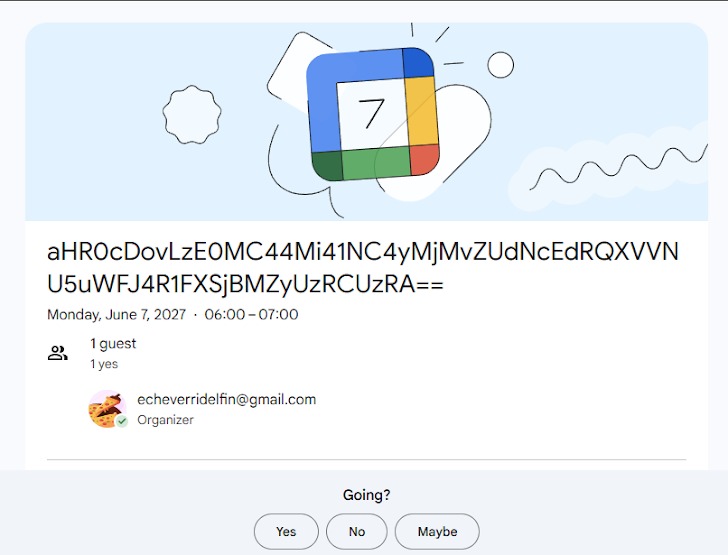
After receiving the Google Calendar link, a series of redirects occur until an HTTP 200 OK response is received. Then, the data-base-title attribute containing a base64-encoded URL pointing to the final payload is extracted from the event HTML page.
The response body contains a base64-encoded payload executed at the second stage of the attack; apparently, the initialization vector and secret key are passed in the HTTP headers, which indicates that the final payload can be encrypted.
The fetched payload is then Base64-decoded and executed via eval(.The script is saved to a temporary folder to prevent simultaneous execution of multiple instances.
Interestingly, Veracode experts were unable to extract and examine the final payload; they believe that the campaign could be temporarily inactive or still at early development stages.
The researchers have already notified npm of their findings; however, the above-listed malicious packages weren’t removed from the platform yet.
