Analysts at F6 discovered a network of domains used by the group NyashTeam, which distributes malware and provides hosting services to criminals. The group’s clients have attacked users in at least 50 countries worldwide, including Russia. More than 110 domains in the .ru zone used by NyashTeam have been blocked.
NyashTeam has been active since at least 2022 and operates in the field of MaaS (Malware-as-a-Service). The group sells malware from the DCRat and WebRat families through Telegram bots and websites, and also provides hosting services for cybercriminal infrastructure, offering customer support via plugins, guides, and data processing tools.
It is noted that most of the targets attacked by the attackers using NyashTeam’s tools were located in Russia, and the group primarily focuses on a Russian-speaking audience.
NyashTeam gained popularity due to the relatively low cost of their malware. For instance, a subscription to the backdoor DCRat (designed for remote control of infected devices) is priced at 349 rubles per month. A monthly subscription to WebRat (used for stealing data from browsers, including passwords, cookies, and autofill information) costs 1,199 rubles, while web hosting is 999 rubles for two months. The attackers accept payments through Russian payment systems as well as cryptocurrency wallets.
Researchers report that in most cases, the group’s clients distribute malware via YouTube and GitHub. The attacks primarily target gamers looking for cheats, as well as users wanting to download software for free.
On YouTube, attackers use fake or compromised accounts to upload videos promoting game cheats, software cracks, and game bots. The links under such videos direct users to file-sharing sites, where under the guise of cheats and cracks, they are offered to download an archive containing malware. On GitHub, NyashTeam’s malicious software is disguised as cracked versions of licensed software, utilities, or cheats, and is hosted in public repositories.
To provide hosting services for malware distribution, NyashTeam actively registers second-level domains, including in the .ru zone. Hackers predominantly use distinctive domain names such as “nyanyash[.]ru”, “nyashback[.]ru”, “nyashk[.]ru”, “nyashka[.]top”, “nyashkoon[.]ru”, “nyashlife[.]ru”, “nyashnyash[.]ru”, “nyashprivat[.]ru”, “nyashru[.]ru”, “nyashteam[.]ru”, “nyashteam[.]site”, “nyashteam[.]top”, “nyashtop[.]ru”, “nyashvibe[.]ru”, “nyashware[.]ru”, “n9sh[.]top”, “n9shteam[.]in”, “n9shteam[.]ru”, “n9shteam2[.]top”, “renyash[.]ru”, “devnyash[.]top”, “devnyashk[.]ru”, “shnyash[.]ru”, “nyashteam[.]ml” or names containing malware names like “webrat” and “dcrat”, and based on these, they create third-level domains.
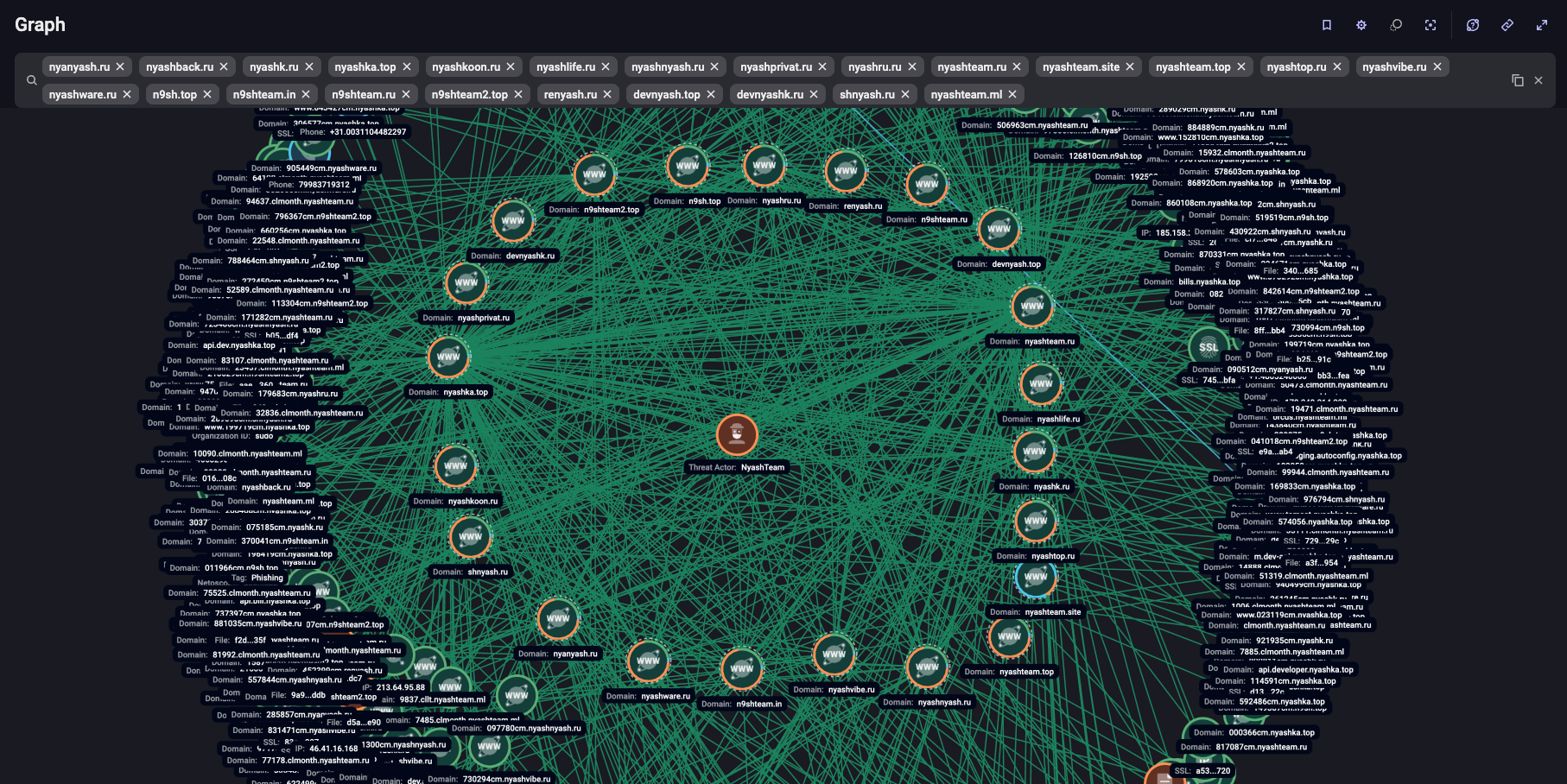
According to F6, since the start of NyashTeam’s activities in 2022, more than 350 second-level domains have been involved in their infrastructure. The peak of malicious domain registration activity occurred in December 2024 and January-February 2025.
At the same time, experts noted not only an active increase in the number of domains used by NyashTeam but also their use in attacks. For example, in 2024, the group’s clients sent phishing emails with DCRat to Russian companies operating in the fields of logistics, oil and gas extraction, geology, and IT.
CERT-F6 provided information about domains associated with NyashTeam to the Coordination Center for .RU/.РФ Domains. As a result, as of July 21, 2025, more than 110 domains in the .ru zone have been blocked. Four more domains in other zones are in the process of being blocked. It is also reported that a Telegram channel with the source code for WebRat was blocked, as well as four hacker tutorial videos on a popular video hosting platform.
“The NyashTeam case clearly proves that the infrastructure of MaaS operators distributing malware can be detected and effectively blocked. Analyzing and subsequently blocking the domains used by the NyashTeam group allowed us to significantly limit the spread of threats and hinder the criminals’ operations, at least temporarily,” said Vladislav Kugan, cyberattack research analyst in the Threat Intelligence department at F6.