A vulnerability dubbed MadeYouReset has been discovered in several HTTP/2 implementations. This issue can be used to carry out powerful DDoS attacks.
Researchers from Imperva and Deepness Lab, as well as Tel Aviv University, report that the vulnerability has been assigned the primary identifier CVE-2025-8671. However, the bug affects products from various vendors, many of which have already released their own CVEs and security advisories: Apache Tomcat (CVE-2025-48989), F5 BIG-IP (CVE-2025-54500), Netty (CVE-2025-55163), Vert.x and Varnish.
It is also reported that solutions from Mozilla, Wind River, the Zephyr Project, Google, IBM, and Microsoft are vulnerable, which could in various ways put affected systems at risk.
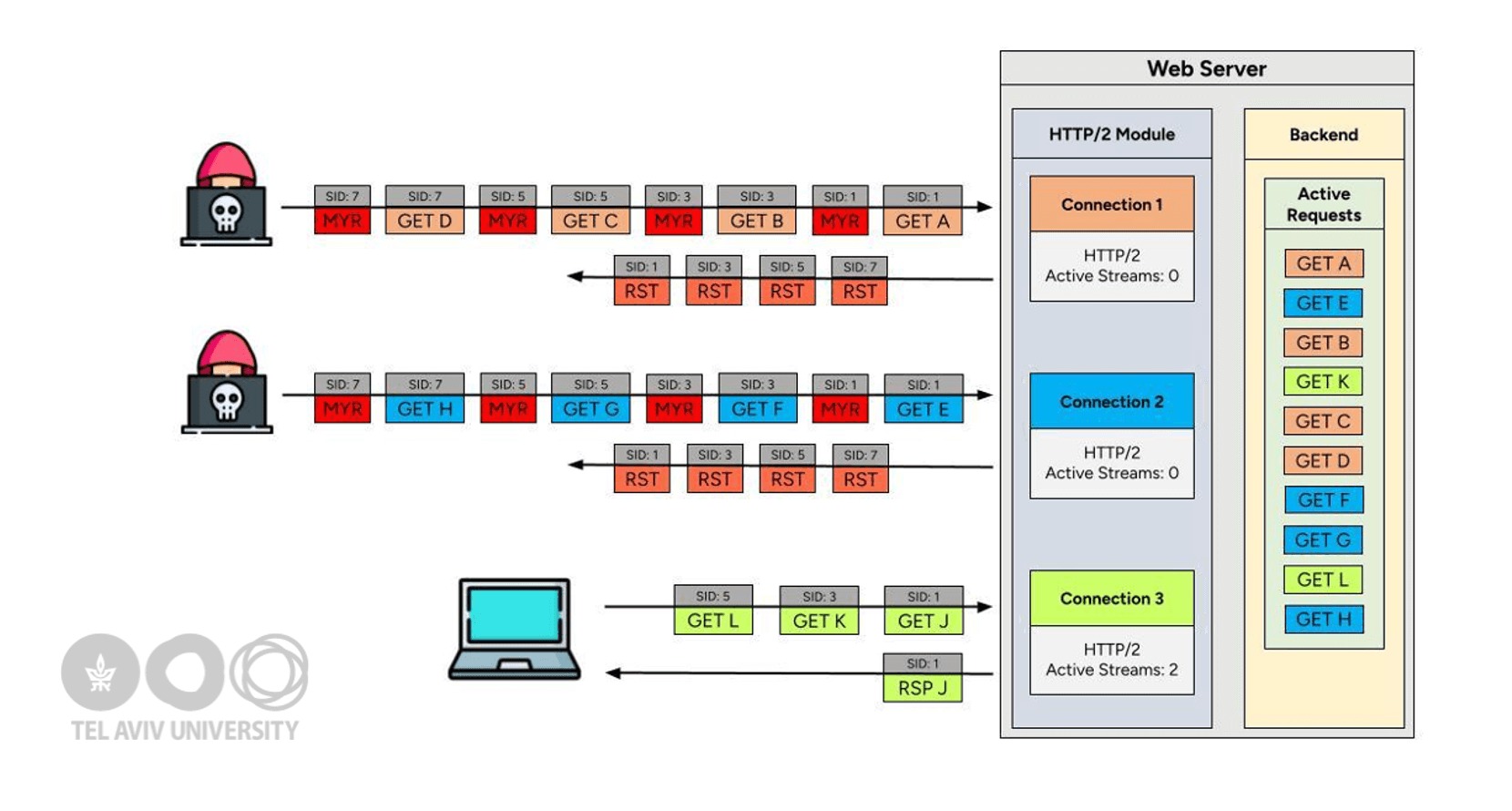
“MadeYouReset bypasses the standard server limit of 100 concurrent HTTP/2 requests per client TCP connection,” the researchers explain. “This limit is intended to protect against DoS attacks by limiting the number of concurrent requests a client can send. With MadeYouReset, an attacker can send many thousands of requests, creating DoS conditions for legitimate users, and in some implementations this can lead to crashes and memory exhaustion.”
The MadeYouReset vulnerability is similar to the Rapid Reset and Continuation Flood issues, which were used in powerful zero-day DDoS attacks and in 2023 broke records for the number of requests per second (RPS).
Like those two attacks that exploit the RST_STREAM and CONTINUATION frames in the HTTP/2 protocol, MadeYouReset is built on top of Rapid Reset and a bypass of the protection that limits the number of streams a client can cancel via RST_STREAM.
The attack exploits a peculiarity whereby the RST_STREAM frame is used both for client-initiated cancellation and for reporting stream errors. MadeYouReset works by sending specially crafted frames that trigger unexpected protocol violations, forcing the server to reset the stream via RST_STREAM.
“For MadeYouReset to trigger, a stream must begin with a valid request that the server starts processing, and then an error must be induced so that the server resorts to RST_STREAM while the backend continues computing the response,” the experts write. “By crafting certain invalid control frames or disrupting the protocol at the right moment, we can force the server to use RST_STREAM for a stream that already contained a valid request.”
The attack is notable in that it frees the attacker from the need to send an RST_STREAM frame and completely bypasses defenses against Rapid Reset, ultimately achieving an effect similar to previous attacks.
In addition, Imperva notes that MadeYouReset blends in with regular traffic, making such attacks difficult to detect.
Experts recommend a set of measures to help protect against MadeYouReset, including stricter protocol validation, deploying tighter stream state tracking to reject invalid transitions, implementing rate limiting at the connection level, and deploying anomaly detection and behavioral monitoring systems.
“MadeYouReset serves as a reminder that even well-formed traffic can be weaponized if we don’t examine it closely enough,” Imperva emphasizes.
