The Python Software Foundation team reported that it has revoked all PyPI tokens stolen during the GhostAction supply chain attack that occurred in early September. The specialists emphasized that the attackers did not use the tokens to publish malware.
Recall that in early September, researchers from GitGuardian discovered that malicious GitHub Actions workflows (for example, FastUUID) were attempting to steal PyPI tokens by sending them to a remote server. The GitGuardian team emailed the PyPI security staff the same day, but the message ended up in spam, delaying the response to the incident until September 10.
According to GitGuardian’s estimate, more than 3,300 secrets were stolen during the GhostAction attack, including PyPI, npm, DockerHub, and GitHub tokens, Cloudflare and AWS API keys, and database credentials.
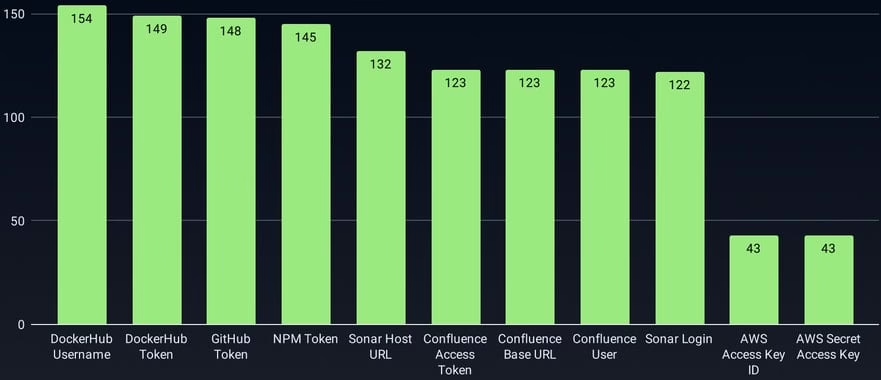
As soon as GitGuardian understood the full scope of what was happening, the company opened issues on GitHub in more than 570 affected repositories and notified the security teams at GitHub, npm, and PyPI about the incident.
Many project maintainers independently rotated their PyPI tokens, reverted changes, or deleted the affected workflows after receiving the notifications.
Although the PyPI team reports that it found no evidence of PyPI repositories being compromised, it decided to revoke all affected tokens. The specialists also contacted the owners of projects impacted by the attack to help them secure their accounts.
As PyPI administrator Mike Fiedler reports, PyPI package maintainers who use GitHub Actions are advised to replace long-lived tokens with Trusted Publishers short-lived tokens, which can help protect against similar attacks. He also urged everyone to log into their accounts and review their history for any suspicious activity.
“It appears the attackers targeted a wide range of repositories—many of which contained PyPI tokens stored as GitHub Secrets—by modifying their workflows to send the tokens to external servers. Although the attackers successfully stole some tokens, it seems they did not use them on PyPI,” Fidler writes.
