The primary purpose of the new feature is to detect rogue tech support pages. Such malicious websites deceive users by convincing them that their computer is infected with a virus or has other problems. The warnings are displayed in full-screen or pop-up windows that are difficult to close.
The scammers provoke the victim to call the number provided and ask for help; their goal is to trick that person into paying for unnecessary services or software. In addition, scammers try to gain remote access to victim’s device, which can result in financial losses or data theft.
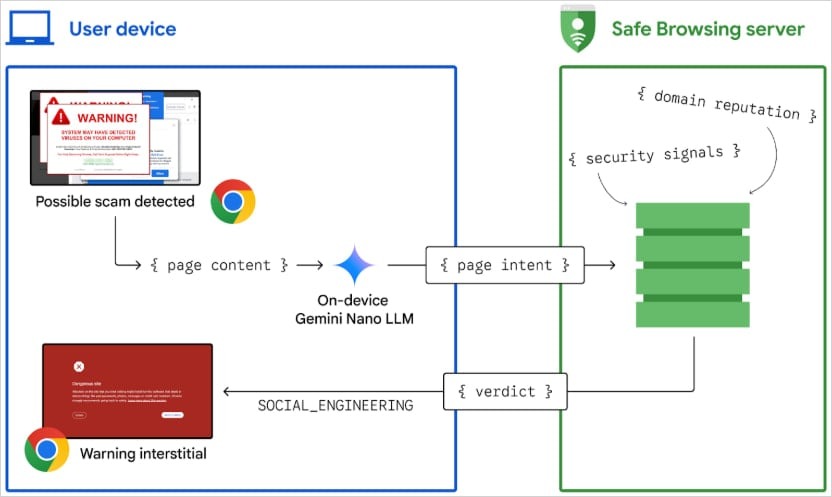
The new anti-scam protection system is integrated into the Enhanced Protection mode of Safe Browsing; it analyzes web pages in real time to detect signs of scam (e.g. fake virus warnings and full-screen windows) typical for technical support scams.
The analysis is performed autonomously and locally on the user’s device using Gemini Nano. If potential scam is detected, the data are sent to Google Safe Browsing for a final verdict. If Safe Browsing confirms scam, Chrome displays an interstitial warning page to notify the user of the risk.
Google developers claim that the new feature doesn’t affect performance and user privacy (although no technical details are provided in the announcement).
“This is all done in a way that preserves performance and privacy. In addition to ensuring that the LLM is only triggered sparingly and run locally on the device, we carefully manage resource consumption by considering the number of tokens used, running the process asynchronously to avoid interrupting browser activity, and implementing throttling and quota enforcement mechanisms to limit GPU usage,” – Google.
The new AI-based protection feature has already been implemented in Chrome 137 released this week; by default, it will be enabled for all users who update to the latest version and enable Enhanced Protection in Settings.
In the future, Google intends to expand this system so that it can detect other types of scam (e.g. package tracking scams and unpaid toll scams). In 2025, the company is going to introduce similar functionality to the Chrome browser for Android.
