The maintainers of NX warned users about a supply chain attack dubbed s1ngularity that occurred on August 26, 2025. The compromise of one developer’s token allowed the attackers to publish malicious versions of the popular npm package and other tools, and then steal user data.
NX is a popular open-source build platform that helps manage code in large projects. It positions itself as “an AI-first build platform that brings together everything — from the editor to CI.” The project has over 4 million weekly downloads.
“Malicious versions of the nx package, as well as some auxiliary plugins, were published to npm. They included code that scans the file system, collects credentials, and sends them to GitHub as a repository under the user’s account,” reads the official statement from the maintainers.
The developers explain that the root cause of the compromise was a vulnerable workflow, added on August 21, 2025, which allowed executable code to be injected via a specially crafted pull request header. Although this workflow was rolled back “almost immediately” after the issue was discovered, the attacker managed to create a pull request to trigger the attack, targeting an outdated branch that still contained the vulnerable workflow.
“The pull_request_target trigger was used to run an action when a pull request was created or modified,” the NX team writes. “However, a warning was overlooked: unlike the standard pull_request, this trigger runs the workflow with elevated privileges, including a GITHUB_TOKEN with read and write permissions to the repository.”
It is assumed that in the end the GITHUB_TOKEN was used to trigger publish.yml, which is responsible for publishing NX packages to the registry using an npm token.
Since the pull request validation workflow was running with elevated privileges, the attackers were able to trigger the publish.yml workflow in the nrwl/nx repository with their malicious changes. This allowed them to steal the npm token by sending it to an endpoint they controlled on webhook[.]site.
“As part of the bash injection, the pull request validation workflow triggered publish.yml with this malicious commit and sent our npm token to an unknown webhook,” the developers write. “We believe this is how the attacker obtained the npm token used to publish the malicious versions of nx.”
The list of affected packages and versions is given below. They have currently been removed from npm.
- nx 21.5.0, 20.9.0, 20.10.0, 21.6.0, 20.11.0, 21.7.0, 21.8.0, 20.12.0
- @nx/devkit 21.5.0, 20.9.0
- @nx/enterprise-cloud 3.2.0
- @nx/eslint 21.5.0
- @nx/js 21.5.0, 20.9.0
- @nx/key 3.2.0
- @nx/node 21.5.0, 20.9.0
- @nx/workspace 21.5.0, 20.9.0
In the malicious versions of the packages, a postinstall script was discovered that activated after installation, scanned the system for text files, collected credentials, and exfiltrated the gathered data, encoded in base64, to publicly accessible GitHub repositories named s1ngularity-repository (or s1ngularity-repository-0 and s1ngularity-repository-1) using the user’s account.
“The malicious postinstall script also modified the .zshrc and .bashrc files, which are executed when the terminal launches, adding sudo shutdown -h 0, which prompts users for the system password and, if provided, immediately shuts down the machine,” the maintainers add.
Although GitHub is already removing such repositories, users who encountered the attack are advised to assume their information is compromised and urgently change their credentials, as well as rotate their GitHub and npm tokens. It’s also recommended to stop using the malicious packages as soon as possible and check the .zshrc and .bashrc files for unfamiliar instructions and remove them.
The NX team reports that it has already rotated its npm and GitHub tokens, audited GitHub and npm activity for suspicious behavior, and updated NX publishing permissions to require two-factor authentication.
Researchers from the cybersecurity company Wiz report that 90% of the GitHub tokens stolen by the hackers are still valid, as are dozens of valid cloud credentials and npm tokens.
According to experts, the malware was often executed on developers’ machines via the NX extension for Visual Studio Code.
As StepSecurity notes, this incident was the first known case in which attackers turned command-line AI tools (Claude, Google Gemini, and Amazon Q) into a weapon for exploiting the software supply chain and used them to bypass defenses.
“They made AI tools recursively scan the file system and write the discovered sensitive file paths to /tmp/inventory.txt, effectively using legitimate tools as accomplices in the attack,” StepSecurity says.
At the same time, the repositories containing the stolen secrets remained active and publicly accessible for roughly eight hours, until GitHub representatives intervened in the situation.
Meanwhile, experts at GitGuardian reported that they found 1,346 repositories containing the string “s1ngularity-repository.” New ones are still appearing, meaning developers continue to use the compromised package. Attackers now appear to be using compromised GitHub tokens to make previously private repositories public and rename them following the pattern s1ngularity-repository-#5characters#.
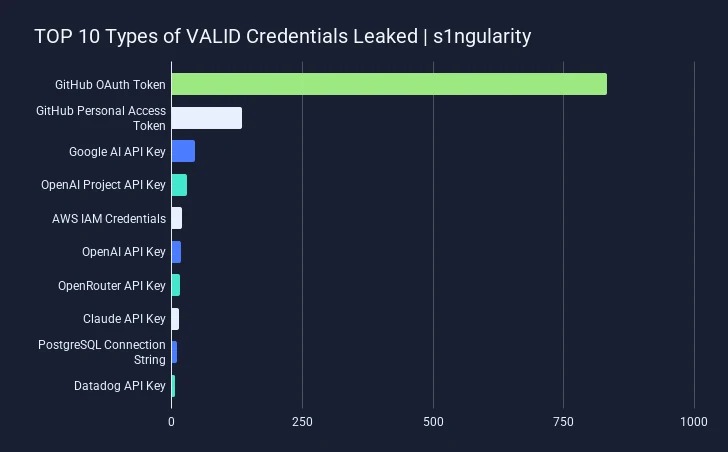
According to the researchers’ estimates, among the 2,349 stolen secrets, the vast majority are GitHub OAuth keys and personal access tokens (PAT), followed by API keys and credentials for Google AI, OpenAI, Amazon Web Services, OpenRouter, Anthropic Claude, PostgreSQL, and Datadog.
It is noted that 85% of the infected systems were running macOS.
