The ransomware hacking group Interlock is distributing a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) through compromised websites. The hackers use FileFix attacks to deliver the malware.
ClickFix Attacks are built on social engineering. Recently, various variations of these attacks have become common. Typically, victims are lured to fraudulent websites and are tricked into copying and executing malicious PowerShell commands. In other words, they are made to infect their own system with malware manually.
Attackers explain the need to execute certain commands as a solution to problems with displaying content in the browser or demand that the user solve a fake CAPTCHA.
Although ClickFix attacks most often target Windows users, convincing them to execute PowerShell commands, cybersecurity specialists have already warned of campaigns targeting macOS and Linux users as well.
According to ESET, the use of ClickFix as an initial access vector has increased by 517% from the second half of 2024 to the first half of 2025.
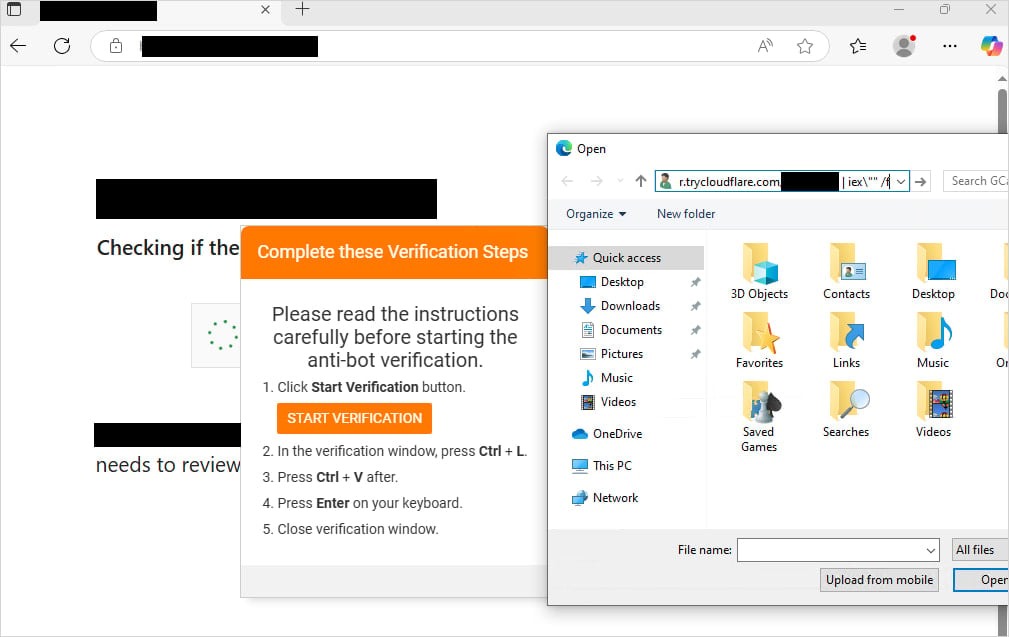
The FileFix technique, recently described by cybersecurity expert mr.d0x, is a variant of the ClickFix attack. However, instead of using the command line, it utilizes the more user-friendly Windows File Explorer interface.
On the malicious page, the user is informed that they have been granted shared access to a certain file. To find this file, it is supposedly necessary to copy the path and paste it into “File Explorer”.
“A phishing page may contain an ‘Open Explorer’ button, which, when clicked, will launch File Explorer (using file download functionality) and copy a PowerShell command to the clipboard,” explained mr.d0x.
This means that after inserting the file path and pressing Enter, the malicious PowerShell command will be executed.
As early as May 2025, experts from The DFIR Report and Proofpoint warned that Interlock RAT was being distributed via KongTuke (or LandUpdate808)—a sophisticated traffic distribution system (TDS). This results in malware infection through a multi-step process that includes the use of ClickFix and fake CAPTCHA challenges.
According to new information, hackers switched to using FileFix in early June and began distributing a PHP variant of the Interlock RAT. Experts from The DFIR Report indicate that in some cases, a Node.js variant of the malware is also being spread.
This is the first publicly documented instance of the FileFix technique being used in real-world attacks.
After execution, the RAT collects system information using PowerShell commands to gather and transmit data to its operators. The malware also checks what privileges the logged-in user holds.
The RAT establishes itself in the system and awaits further commands for execution. The specialists’ report notes that attackers are clearly operating the malware manually, checking backups, navigating through local directories, and inspecting domain controllers. Researchers point out that in some cases, the attackers used RDP for lateral movement within compromised environments.
As a command server, the malware exploits trycloudflare.com, abusing the legitimate Cloudflare Tunnel service to conceal its activity.
The DFIR Rep believes that this campaign is opportunistic in nature.
