Nvidia recommends users activate System Level Error-Correcting Code (ECC), as graphics cards with GDDR6 memory are vulnerable to the Rowhammer attack.
“The risk of successfully exploiting the Rowhammer vulnerability depends on the DRAM model, platform, architectural features, and system settings,” the manufacturer reports.
Recall that the original Rowhammer attack was devised in 2014 by experts from Carnegie Mellon University. Its essence was based on the fact that intensive manipulation of certain memory cells could cause a change in the bit state of adjacent cells.
Memory cells store information in the form of electrical charges, which determine bit values as 1 or 0. Due to increased cell density, repeated “hammering” (when an application accesses the same areas thousands of times within fractions of a second) can alter the charge state in adjacent rows, leading to “bit flipping.” This phenomenon is where the name Rowhammer comes from.
Such deliberate bit flips can be used by attackers who ultimately gain access to confidential data, can decrypt and tamper with it, as well as exploit the issue remotely, escalate privileges, and more.
The advisory released by Nvidia is related to a new study published by experts from the University of Toronto. The researchers demonstrated that Rowhammer can be adapted to attack the Nvidia A6000. This attack has been named GPUHammer.
Although carrying out a Rowhammer attack on GDDR6 is more challenging — due to greater latency and faster refresh compared to DDR4 in regular RAM — researchers have proven that such attacks on GPUs are generally possible.
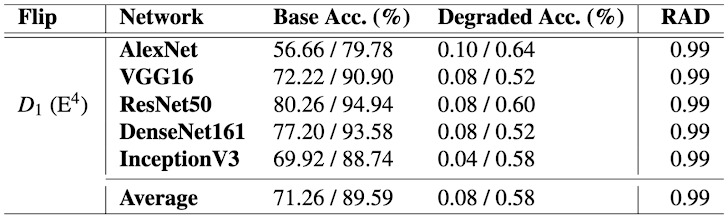
“We executed GPUHammer on an Nvidia RTX A6000 (48 GB GDDR6), tested four memory banks (DRAM), and recorded eight different single-bit flips (failures occurred in all tested banks),” the specialists write. “The minimum number of activations (TRH) required to induce a flip was about 12,000, which aligns with previous observations for DDR4. Using these flips, we conducted the first-ever Rowhammer attack on a GPU, which reduces the accuracy of machine learning models.”
GPUHammer can reduce the accuracy of an AI model from 80% to 0.1% with just a single bit flip on an A6000 GPU.
The aforementioned error-correcting codes (System Level Error-Correcting Codes, ECC) help maintain data integrity by adding redundant bits and correcting single-bit errors to ensure data reliability and accuracy.
For graphics cards designed for workstations and data centers, where VRAM handles large data sets and precise computations related to AI, System Level ECC should be enabled to prevent critical errors.
In its security bulletin, Nvidia highlights that researchers from the University of Toronto demonstrated a “potential Rowhammer attack on the Nvidia A6000 GPU with GDDR6 memory,” where the System Level ECC feature was disabled.
In addition to the RTX A6000, Nvidia also recommends enabling System Level ECC for the following products.
Graphics Cards for Data Centers:
- Ampere — A100, A40, A30, A16, A10, A2, A800;
- Ada — L40S, L40, L4;
- Hopper — H100, H200, GH200, H20, H800;
- Blackwell — GB200, B200, B100;
- Turing — T1000, T600, T400, T4;
- Volta — Tesla V100, Tesla V100S.
Graphics Cards for Workstations:
- Ampere RTX — A6000, A5000, A4500, A4000, A2000, A1000, A400;
- Ada RTX — 6000, 5000, 4500, 4000, 4000 SFF, 2000;
- Blackwell RTX PRO;
- Turing RTX — 8000, 6000, 5000, 4000;
- Volta — Quadro GV100.
Embedded and industrial solutions:
- Jetson AGX Orin Industrial;
- IGX Orin.
At the same time, Nvidia notes that newer GPUs, including the Blackwell RTX 50 Series (GeForce), Blackwell Data Center GB200, B200, B100, and Hopper Data Center H100, H200, H20, and GH200, are equipped with built-in ECC protection, which does not require user intervention.
It is worth noting that, according to the researchers’ estimates, enabling System Level ECC may slow down the performance of AI models by 10% and also reduce the available memory capacity by up to 6.5% under any type of load.