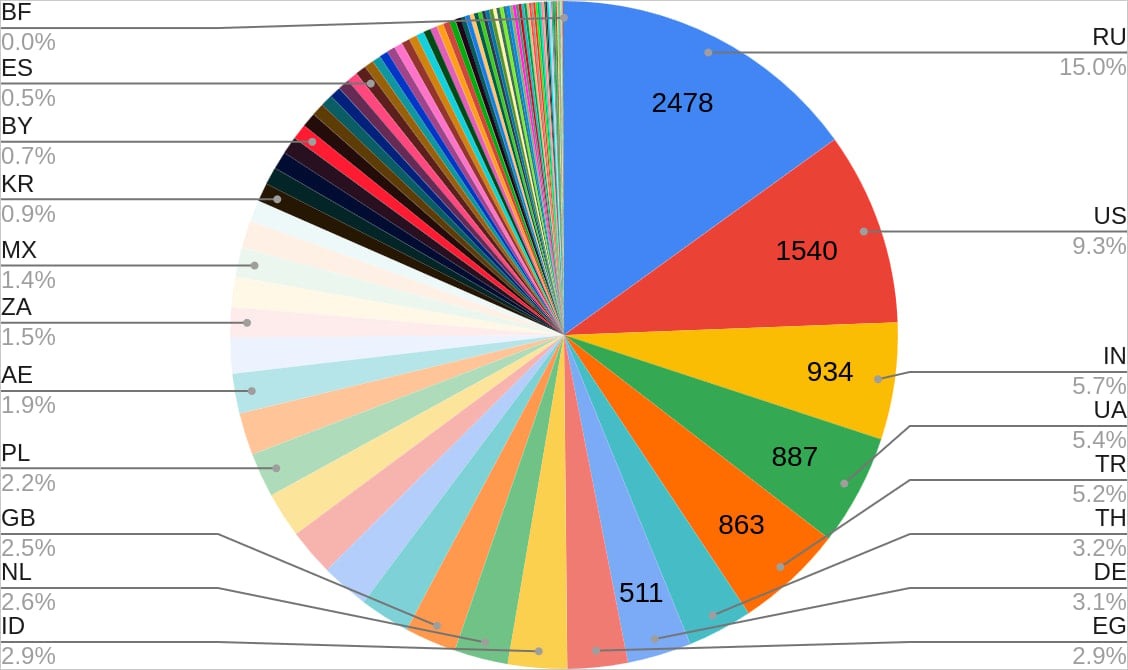
In total, 18,459 devices worldwide were affected by such attacks; most of them are located in Russia, USA, India, Ukraine, and Turkey.
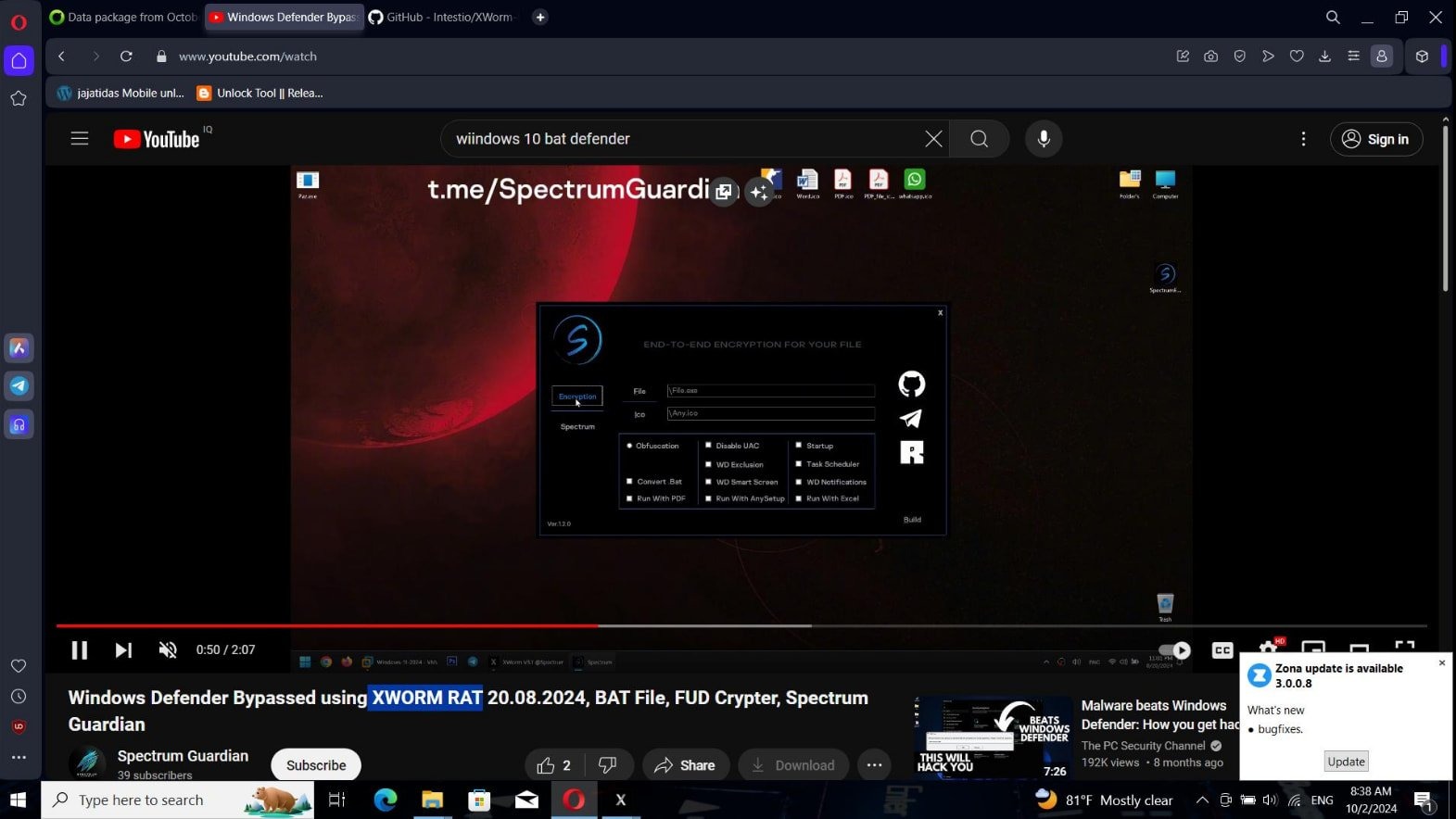
“A trojanized version of the XWorm RAT builder has been weaponized and propagated, – CloudSEK specialists say. – It is targeted specially towards script kiddies who are new to cybersecurity and directly download and use tools mentioned in various tutorials thus showing that there is no honor among thieves”.
The malware has a ‘switch’ that has already been activated to uninstall it from infected computers. However, due to certain restrictions, many systems remain compromised.
The infected builder is propagated in a variety of ways, including GitHub repositories, file sharing platforms, Telegram channels, YouTube videos, and various websites. All these sources advertise XWorm RAT as a free hacker tool.
However, in reality, the builder contains malware that checks the Windows registry for Virtualization and stops working if the result is positive. If the host meets the infection criteria, the malware makes the required changes in the registry to gain a foothold in the system. Each infected PC is registered on the Telegram control server using a hardcoded identifier and a Telegram bot token.
Then the malware steals Discord tokens, system info, and location data (based on the IP address) from the unfortunate hacker’s computer and transmits them to the attackers’ server. After that, the malware waits for further commands from its operators.
Overall, the backdoor supports 56 commands, including:
/machine_id*browsers – grab browser data;
/machine_id*keylogger – get user keylogs;
/machine_id*desktop – grab a screenshot твы;
/machine_id*encrypt*
/machine_id*processkill*
/machine_id*upload*s t work if the file is too big); and
/machine_id*uninstall – uninstall RAT from victim`s PC.
According to CloudSEK, the malware operators have stolen data from some 11% of infected devices: mostly, by taking screenshots and intercepting browser information.
CloudSEK specialists tried to destroy this botnet using hardcoded API tokens and its built-in ‘kill switch’ whose purpose is to remove the malware from infected devices. To do this, they sent the uninstall command to all known clients using IDs of infected machines extracted from Telegram logs. The researchers also brute-forced IDs from 1 to 9999 since the attackers could employ a simple numeric pattern.
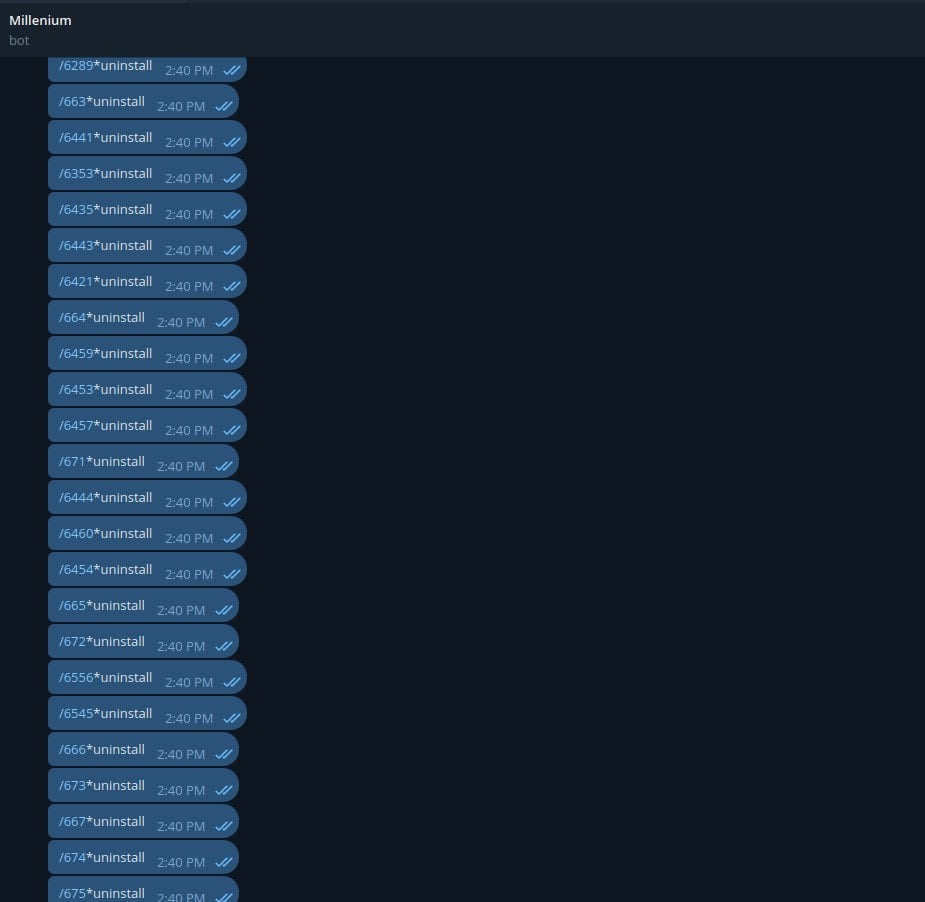
This measure made it possible to remove the backdoor from many infected systems, but computers that were offline when the command was sent remained compromised. In addition, some malware uninstall commands could be lost in transit due to Telegram’s messaging restrictions.
CloudSEK experts emphasize that hackers hack other hackers on a regular basis. Therefore, you should never trust unsigned software, especially distributed by cybercriminals; while operations involving malware builders should be performed only in test and analytical environments.
