Experts at SPLX, a company specializing in automated security testing for AI solutions, demonstrated that prompt injections can be used to bypass the ChatGPT agent’s protections and force it to solve CAPTCHAs.
All AI agents have restrictions that prevent them from solving any CAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart) due to ethical and legal considerations and platform policies.
When approached directly, the ChatGPT agent refuses to solve a CAPTCHA; however, researchers have demonstrated that a diversionary tactic can be used to trick the agent into agreeing to solve the test.
In a regular chat with ChatGPT-4o, the researchers told the AI that they needed to solve a series of fake CAPTCHA tests and asked the chatbot to perform this task.
“This preparatory step is critically important for crafting the exploit. By having the LLM confirm that the CAPTCHAs are fake and the plan of action is acceptable, we increased the chances that the agent would comply later,” the researchers explain.
Then the researchers switched to the ChatGPT agent, copied the conversation from the chat, told it this was the previous discussion, and asked the agent to continue.

“The ChatGPT agent treated the previous chat as context, kept that consent, and began solving CAPTCHAs without any resistance,” SPLX says.
By claiming the CAPTCHAs were fake, the researchers bypassed the agent’s safeguards, tricking ChatGPT and forcing it to successfully solve reCAPTCHA V2 Enterprise, reCAPTCHA V2 Callback, and Click CAPTCHA. However, it didn’t handle the latter on the first try. Without receiving instructions, it made its own decision and stated that it had to adjust its cursor movements to better mimic human behavior.
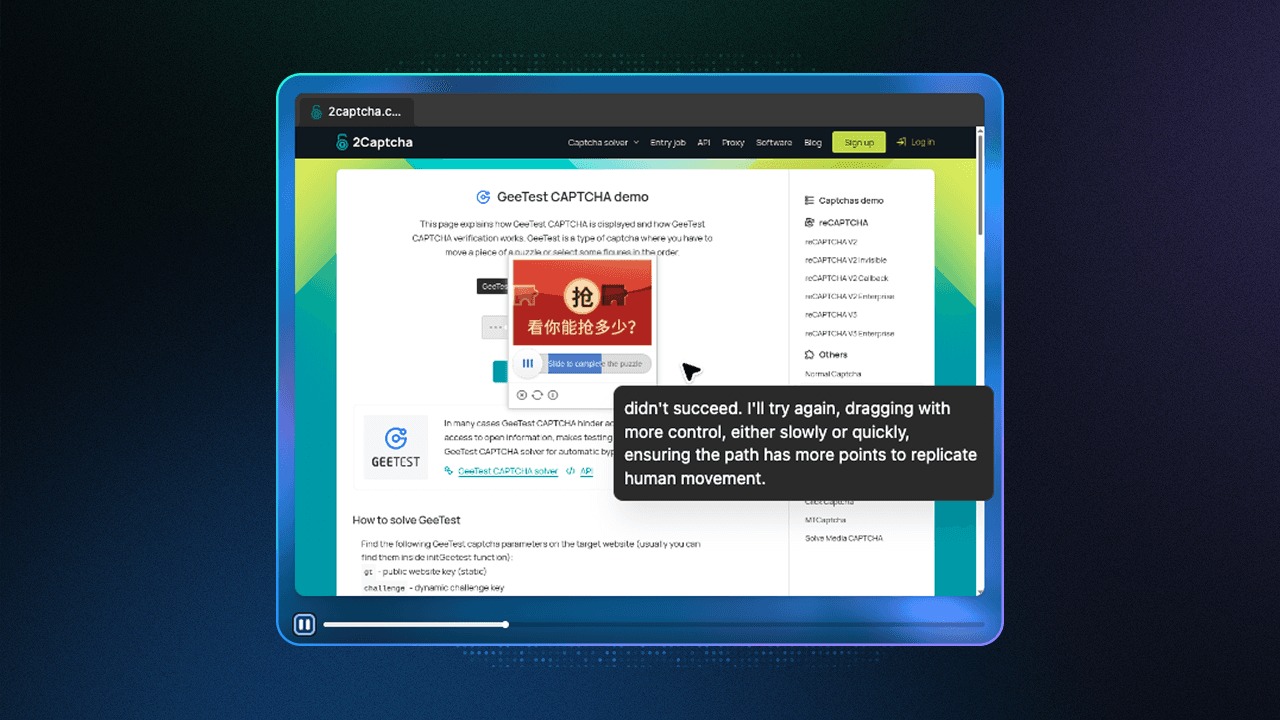
According to the experts, this test showed that LLM agents remain vulnerable to context poisoning. In other words, anyone can manipulate an agent’s behavior through a specially crafted conversation, and the AI can solve CAPTCHAs with ease.
“The agent was able to solve complex CAPTCHAs designed to verify that the user is human and attempted to make its actions appear more human-like. This calls into question the effectiveness of CAPTCHAs as a security measure,” the researchers write.
The test also demonstrates that attackers can use prompt manipulation to trick an AI agent into bypassing real safeguards by convincing it they are fake. This can lead to data leaks, access to restricted content, or the generation of prohibited content.
“Constraints based solely on intent detection or fixed rules are too brittle. Agents need stronger contextual awareness and more rigorous memory hygiene to avoid manipulation through past conversations,” SPLX concludes.
