Rapid7 specialists discovered a vulnerability in several versions of OxygenOS (the Android-based OS used on OnePlus devices). The bug allows any installed application to access SMS message data and metadata without permissions or user interaction.
The issue has been assigned CVE-2025-10184, and researchers warn that it remains unpatched. The manufacturer did not respond for a long time to messages from Rapid7 specialists, who had been trying to establish contact since May 2025. As a result, the experts decided to disclose the technical details of the vulnerability along with a proof-of-concept exploit.
The vulnerability arose because OnePlus modified the standard Android Telephony package by adding extra exported content providers, such as PushMessageProvider, PushShopProvider, and ServiceNumberProvider. In the manifest for these providers, READ_SMS is not declared as the writePermission, leaving them open to any app by default, even if it lacks SMS-related permissions.
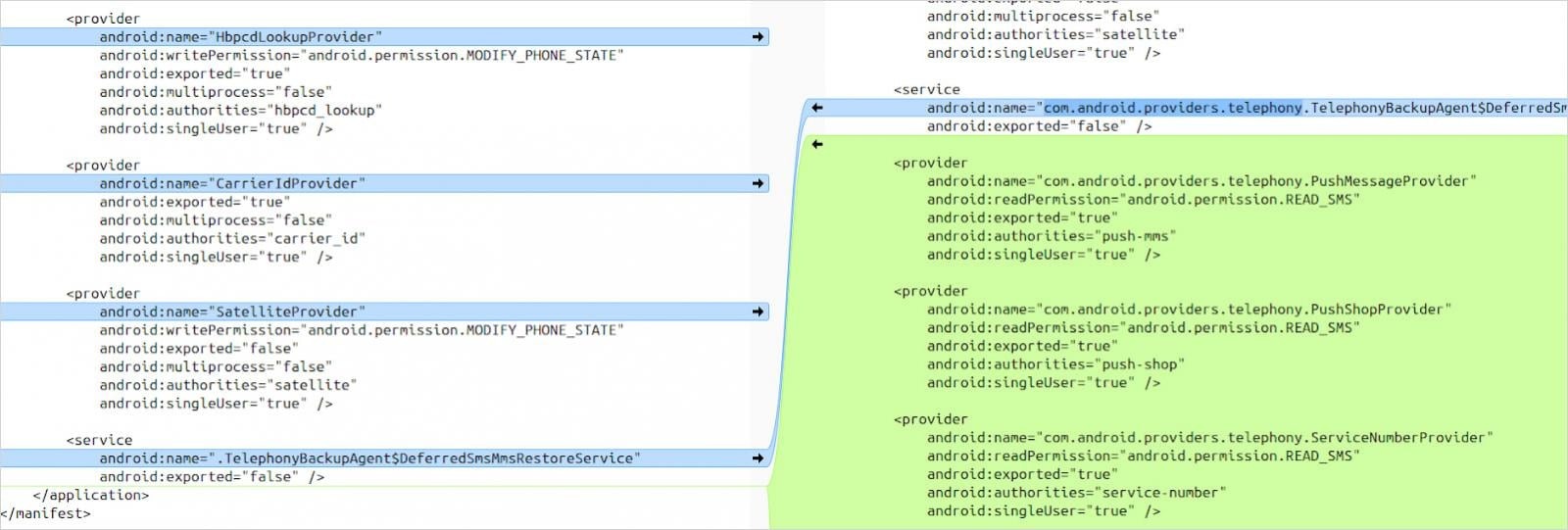
Moreover, user input is not sanitized, which allows so-called blind SQL injections to recover SMS contents from the device’s database by brute-forcing one character at a time.
“By repeating this algorithm for each character in every row returned by the subquery, you can extract the database contents — the return value of the update method will indicate whether your character guess was correct,” Rapid7 explains.
Thus, even though the permission to read SMS is configured correctly, the write permission is not, and this allows SMS content to be extracted under certain conditions:
- the table must contain at least one row so that update() can return a “rows changed” result;
- the provider must allow insert() so that an attacker can create a dummy row for operations if the table is empty;
- the sms table must be located in the same SQLite file, because the injected subquery needs access to it.

The vulnerability affects all versions of OxygenOS from 12 up to the latest 15, built on Android 15. The researchers report that they tested and confirmed the vulnerability on the OnePlus 8T and 10 Pro with various OxygenOS versions and Telephony package versions. It is emphasized that other devices may also be vulnerable.
| Device/Model | Package Version | OxygenOS Version | Build Number |
| OnePlus 8T / KB2003 | 3.4.135 | 12 | KB2003_11_C.33 |
| OnePlus 10 Pro 5G / NE2213 | 14.10.30 | 14 | NE2213_14.0.0.700(EX01) |
| OnePlus 10 Pro 5G / NE2213 | 15.30.5 | 15 | NE2213_15.0.0.502(EX01) |
| OnePlus 10 Pro 5G / NE2213 | 15.30.10 | 15 | NE2213_15.0.0.700(EX01) |
| OnePlus 10 Pro 5G / NE2213 | 15.40.0 | 15 | NE2213_15.0.0.901(EX01) |
“Although the build numbers in the table are specific to the test devices, since the issue affects a core Android component, we expect this vulnerability to also impact other OnePlus devices with the specified OxygenOS versions. In other words, this is not a hardware-specific issue,” the researchers explain.
Shortly after Rapid7’s report was published, OnePlus representatives acknowledged the issue and said they were already looking into it.
Until patches are released, users are advised to minimize the number of apps installed on their OnePlus device, trust only vetted developers, and avoid using SMS-based two-factor authentication in favor of OTP apps (for example, Google Authenticator).
Since SMS on OnePlus devices are not properly isolated yet, confidential communications are recommended only via apps with end-to-end encryption.
