
Researchers at Zscaler discovered that 77 malicious Android applications, with more than 19 million installs in total, were distributing various malware families on the official Google Play store.
“We have seen a sharp increase in the number of malicious adware apps on the Google Play Store, alongside threats like Joker, Harly, and banking trojans such as Anatsa,” the experts write. “At the same time, there has been a noticeable decline in the activity of malware families such as Facestealer and Coper.”
Researchers discovered this campaign during an investigation into a new wave of infections by the Anatsa banking trojan (aka TeaBot), which targets Android devices.
Although most of the malicious apps (over 66%) contained adware, the most common threat turned out to be Joker, which researchers found in nearly 25% of the analyzed apps.
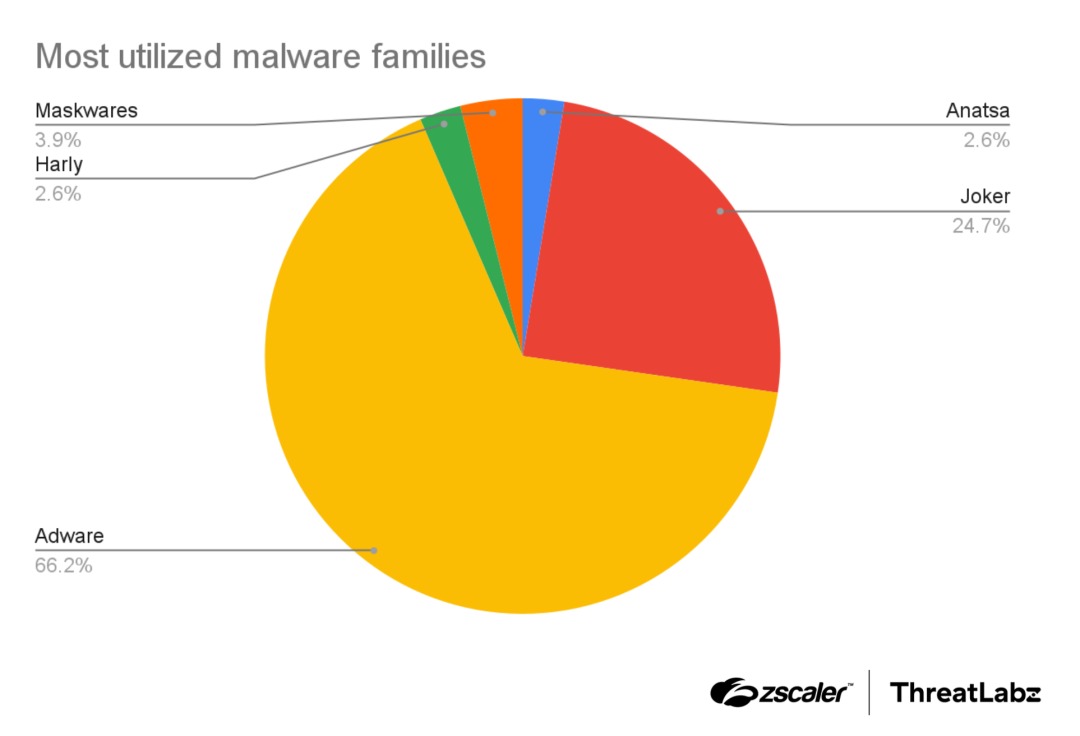
After being installed on a victim’s device, Joker can read and send SMS messages, take screenshots, make phone calls, steal contact lists, access device information, and subscribe users to premium services.
A smaller percentage of the malicious apps were disguised as various harmless programs (researchers referred to such threats as “maskware”). These apps pretend to be legitimate and do offer the features listed in their descriptions; however, they perform malicious activity in the background—stealing credentials, banking information, location data, SMS messages, and so on.
Another variant of the Joker malware dubbed Harly was also discovered; it is a legitimate-looking app with a malicious payload buried deep in the code to evade detection. In March of this year, Human Security researchers warned that Harly could lurk in popular apps such as games, wallpapers, flashlights, and photo editors.
A Zscaler report notes that the latest version of the Anatsa banking trojan can target even more banking and cryptocurrency apps, increasing their number from 650 to 831. The malware downloads phishing pages and a keylogger module from its command-and-control server, and can now target users in Germany and South Korea.
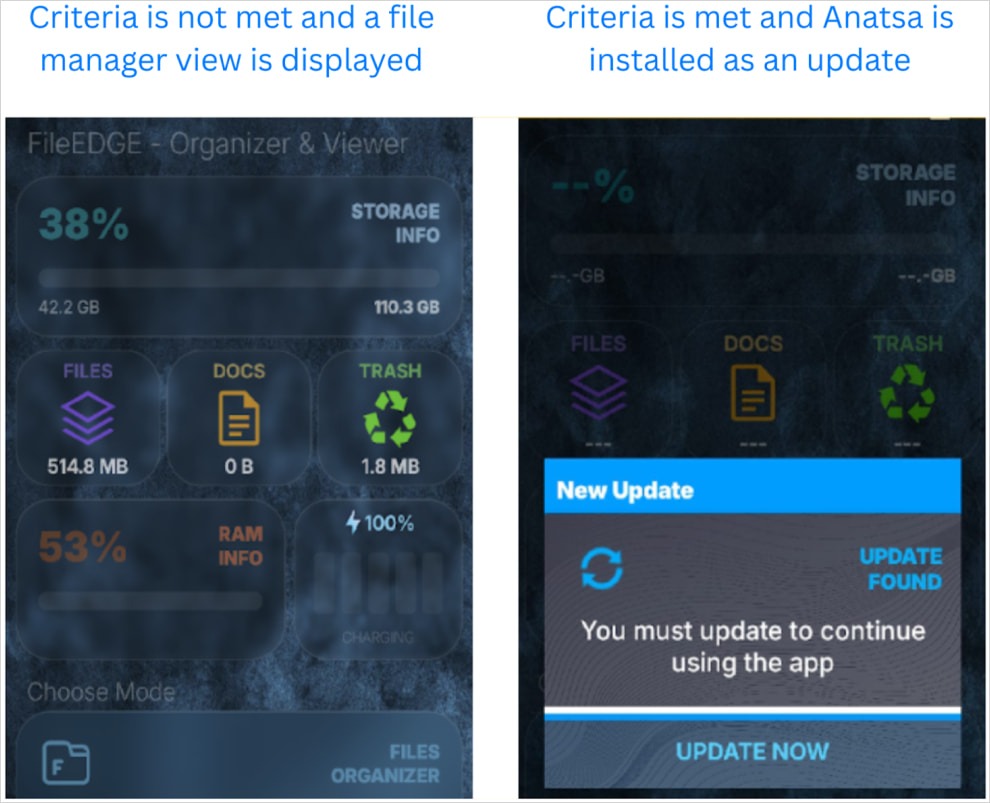
Malware operators use an app called Document Reader – File Manager as a lure; it downloads Anatsa only after installation to bypass Google’s checks.
In addition, in the new campaign the attackers switched from remotely and dynamically loading DEX code to directly installing the malware, unpacking it from JSON files and then deleting them.
To evade static analysis, the Trojan uses corrupted APK archives, DES encryption of strings at runtime, and can detect emulation. Package names and hashes also change periodically.
Zscaler analysts report that, at present, Google has already removed all the discovered malicious apps from the official store.
2025.03.16 — Researchers force DeepSeek to write malware
According to Tenable, the AI chatbot DeepSeek R1 from China can be used to write malware (e.g. keyloggers and ransomware). DeepSeek was released in January 2025 and caused a stir…
Full article →
2025.04.07 — Critical RCE vulnerability discovered in Apache Parquet
All versions of Apache Parquet up to and including 1.15.0 are affected by a critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability whose CVSS score is 10 out…
Full article →
2025.04.10 — April updates released by Microsoft cause issues with Windows Hello
Microsoft warns that some Windows users who have installed the April updates might be unable to login to their Windows services using Windows Hello facial recognition…
Full article →
2025.03.05 — Polish Space Agency disconnects its network due to hacker attack
Last weekend, the Polish Space Agency (POLSA) had to disconnect all of its systems from the Internet to localize an attack targeting its IT infrastructure. After discovering the intrusion,…
Full article →
2025.04.23 — Improper authentication control vulnerability affects ASUS routers with AiCloud
ASUSTeK Computer Inc. fixed an improper authentication control vulnerability in routers with AiCloud. The bug allows remote attackers to perform unauthorized actions on vulnerable devices. The issue…
Full article →
2025.04.25 — Asus patches vulnerability in AMI's MegaRAC enabling attackers to brick servers
Asus released patches for the CVE-2024-54085 vulnerability that allows attackers to seize and disable servers. The security hole affects the American Megatrends International (AMI) MegaRAC Baseboard Management…
Full article →
2025.01.23 — Fake Telegram CAPTCHA forces users to run malicious PowerShell scripts
Hackers used the news of Ross Ulbricht pardoning to lure users to a rogue Telegram channel where they are tricked into running malicious PowerShell code. This…
Full article →
2025.04.12 — Hackers compromised a bureau within the U.S. Department of the Treasury and spent months in hacked systems
The Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), an independent bureau within the United States Department of the Treasury, reported a major cybersecurity incident. Unknown attackers had…
Full article →
2025.02.21 — Microsoft fixes vulnerability in Power Pages exploited by cybercriminals
Microsoft patched a severe privilege escalation vulnerability in Power Pages used by hackers as a 0-day. The vulnerability tracked as CVE-2025-24989 (CVSS score 8.2) pertains…
Full article →
2025.03.12 — Mass exploitation of PHP-CGI vulnerability in attacks targeting Japanese companies
GreyNoise and Cisco Talos experts warn that hackers are actively exploiting CVE-2024-4577, a critical PHP-CGI vulnerability that was discovered and fixed in early June 2024. CVE-2024-457…
Full article →